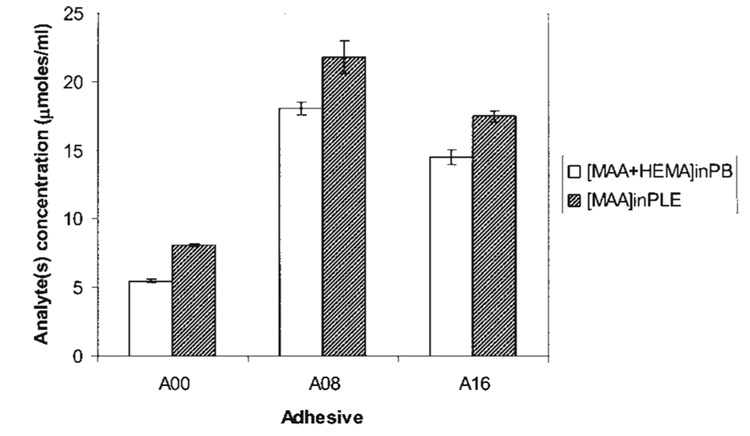
Figure 3.
The cumulative release of MAA in the presence of porcine liver esterase (PLE) was significantly different (p < 0.05) from the sum of analytes [MAA + HEMA] released in the buffer (PB). These differences indicate that MAA formation in the 8-day enzymatic biodegradation study is attributable to hydrolysis of unpolymerized HEMA, pendant groups of bisGMA in the polymer and/or unpolymerized bisGMA. In addition, adhesives simulating wet bonding, A08 and A16 exhibited significantly larger release of analytes compared with the control A00.