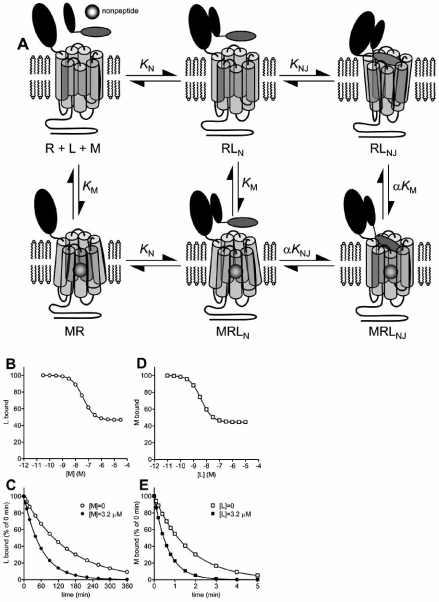
Fig. (3).
Allosteric modulation of peptide binding to Class B GPCR’s via the J-domain. A. Schematic representation of the model. Peptide binding is described by the two domain model (Fig. 1A). Allosteric modulator binds the J-domain of the receptor at a site spatially distinct from the peptide binding regions, defined by the equilibrium constant KM. Binding of modulator allosterically regulates binding of peptide to the J-domain, defined by the cooperativity factor α, without affecting peptide binding to the N-domain. B-E. Manifestation of the model in binding assays for an allosteric inhibitor, simulated using equations in the Appendix. Binding parameters were: KN = 1×108 M-1, [R]TOTAL = 100, KNJ = 2, KM = 1×108 M-1 and α = 0.1 (allosteric inhibition, negative cooperativity). B. Modulation of equilibrium binding of peptide (L) by modulator (M), simulated using eq. 5, [L] = 1×10-9 M. C. Modulation of peptide dissociation by modulator, simulated using eq. 7. The dissociation rate of peptide from the N-domain (k-N) was set at 0.02 min-1. D. Modulation of equilibrium binding of modulator by peptide ligand, simulated using eq. 8, [M] = 2×10-9 M. E. Modulation of modulator dissociation by peptide, simulated using eq. 12. The dissociation rate of modulator (k-M) was set at 0.6 min-1 and the dissociation rate of modulator from MRLNJ (k-M(L)) was set at 6.0 min-1.