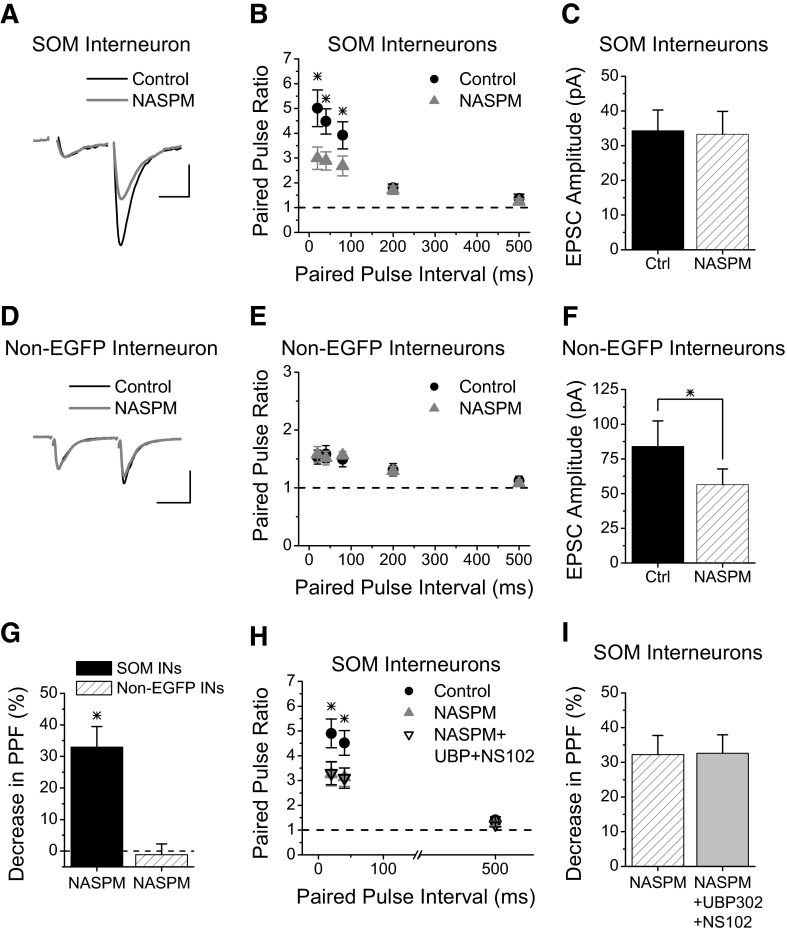
FIG. 3.
Presynaptic kainate receptors are calcium permeable at Schaffer collateral synapses onto SOM interneurons. A: Example of EPSCs recorded from an s. radiatum EGFP-expressing SOM interneuron before and during application of NASPM (200 μM), an antagonist of calcium-permeable AMPA and kainate receptors. Scale bars: 20 ms, 30 pA. B: Group results for paired-pulse ratios showing that blockade of calcium-permeable kainate receptors with application of NASPM reduces paired-pulse facilitation in SOM interneurons at short intervals (n = 12). C: Average amplitude of first EPSC for experiments in B. D: Example of EPSCs recorded from an s. radiatum non-EGFP-expressing interneuron before and during application of NASPM (200 μM). Scale bars: 20 ms, 50 pA. E: Group results for paired-pulse ratios versus interval from non-EGFP-expressing interneurons before and during application of NASPM (n = 10). NASPM caused no change in the paired-pulse facilitation. F: Average amplitude of first EPSC for experiments in E. G: Percent decrease in paired-pulse facilitation with NASPM at 20 ms and 40 ms paired-pulse intervals (combined) for both cell types. H, Group results for paired-pulse ratios versus interval from SOM interneurons for NASPM versus NASPM+UBP302+NS102. Order of application: Control (no drug, black circles), NASPM alone (gray triangles), co-application of NASPM with UBP302 and NS102 (black open triangles). While both NASPM and NASPM+UBP302+NS102 have less paired pulse facilitation compared with Control at 20 and 40 ms, they are not different from each other. I, Percent decrease in paired-pulse facilitation in SOM interneurons (combining 20 ms and 40 ms intervals) for NASPM versus NASPM+UBP302+NS102 (from experiments in H) are not different. * = significant, P < 0.05.