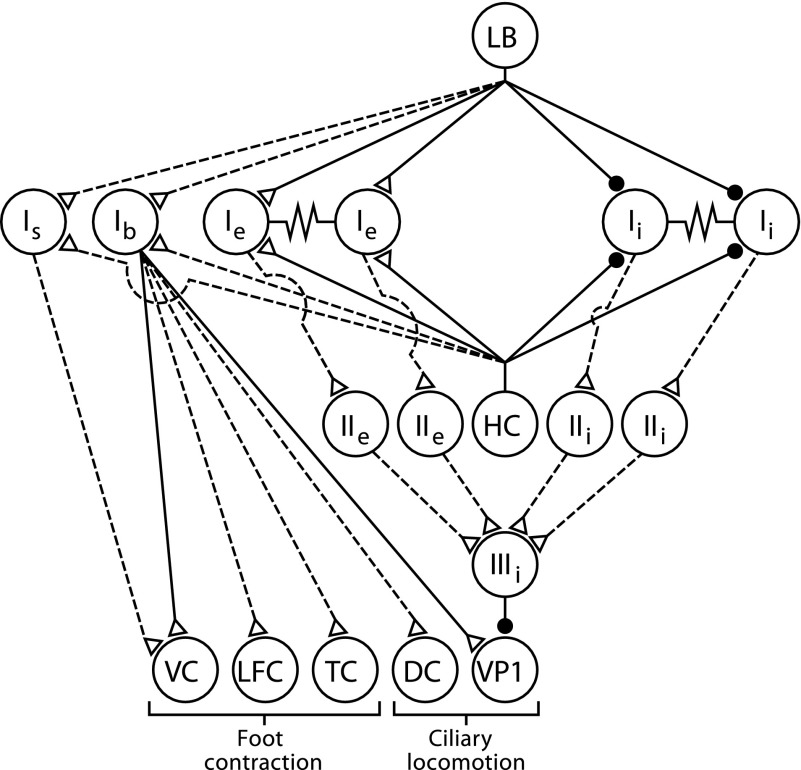
FIG. 9.
Neural circuit supporting ciliary locomotion and foot contraction. Diagram of the sensory neurons, interneurons, efferent neurons, and synaptic connections. The synaptic connections from only one identified photoreceptor [lateral B (LB)] to the type I interneurons is shown. However, each photoreceptor within the eye forms monosynaptic connections with different aggregates of type Ie and type Ii interneurons (Crow and Tian 2000). Statocyst hair cells (HCs) form monosynaptic connections with type I interneurons (Akaike and Alkon 1980). The synaptic connection between type IIIi inhibitory interneurons and ciliary efferent neurons (VP1) are monosynaptic. Type Ib and type Is polysensory interneurons receive input from the visual and graviceptive sensory systems and project to identified foot contractile efferent neurons. Ventral contractile (VC), lateral foot contractile (LFC), tail contractile (TC), and ciliary efferent neurons on the dorsal surface of the pedal ganglia (DC). Filled circles, inhibitory synapses; open triangles, excitatory synapses; solid lines, monosynaptic connections; dashed lines, polysynaptic or synaptic connections where potential monosynaptic inputs have not been tested.