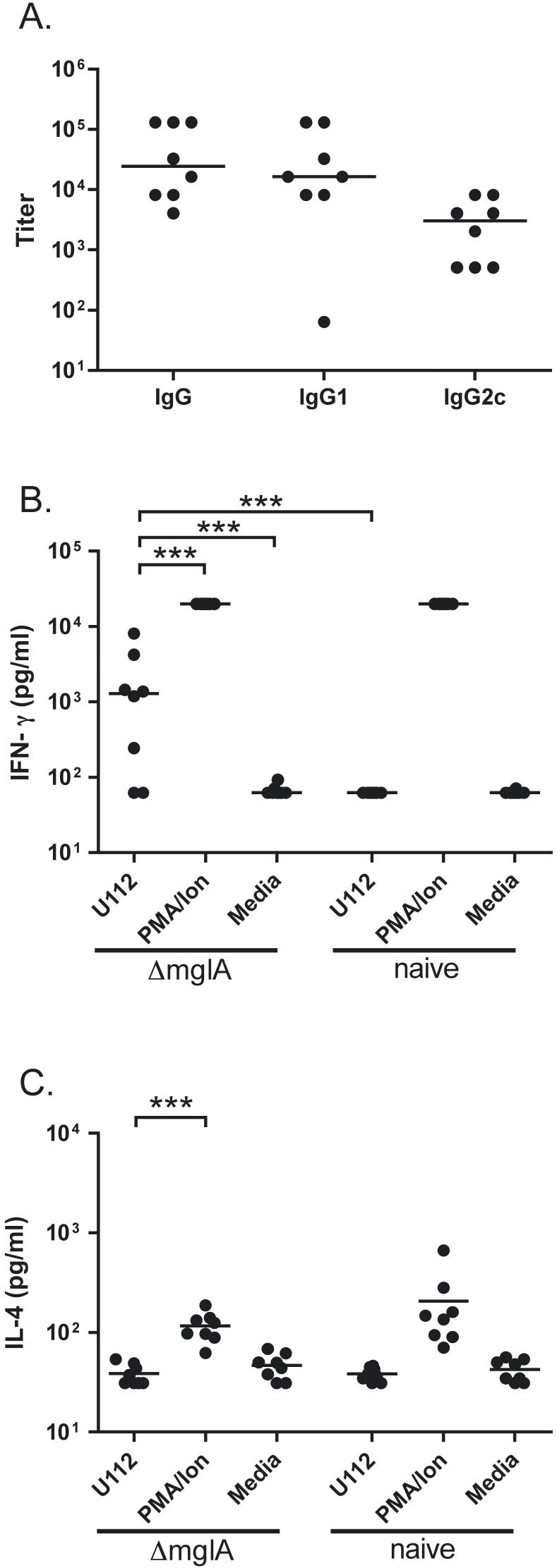
Fig. 4.
F. novicida ΔmglA infection provokes antibody and splenocyte IFN-γ recall responses against U112. A: Serum from C57BL/6 mice 13 days post-aerosol deposition of 104 CFU/lung ΔmglA was assayed in a F. novicida U112 lysate ELISA using goat anti-mouse immunoglobulins conjugated to biotin or to HRP for detection. The data shown combine two independent aerosolization experiments each comprising four mice. B: IFN-γ production was measured in splenocytes harvested from mice 13 days following deposition of 105 CFU/lung ΔmglA or from naïve mice, then plated at 1 × 106 cells per well and stimulated with 1 × 108 CFU/well heat killed U112; 50 ng/ml PMA and 2 μM ionomycin; or media. The limits of detection of the assay were 62.5 pg/ml and 20,000 pg/ml. C: IL-4 production was measured in splenocytes harvested and stimulated in an identical fashion. The limits of detection of the assay were 31.25 pg/ml and 20,000 pg/ml. All cytokine measurements were performed in triplicate on samples from eight mice. Comparable IFN-γ measurements were obtained from two other independent experiments depositing 104 CFU/lung ΔmglA and comparing splenocyte recall responses between four infected and two naive mice. For all panels, bars indicate median values. For cytokine measurements, *** indicates p<0.001 between groups by log transformation and ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. For clarity, only significant differences comparing U112-stimulated splenocytes from ΔmglA-infected mice are shown.