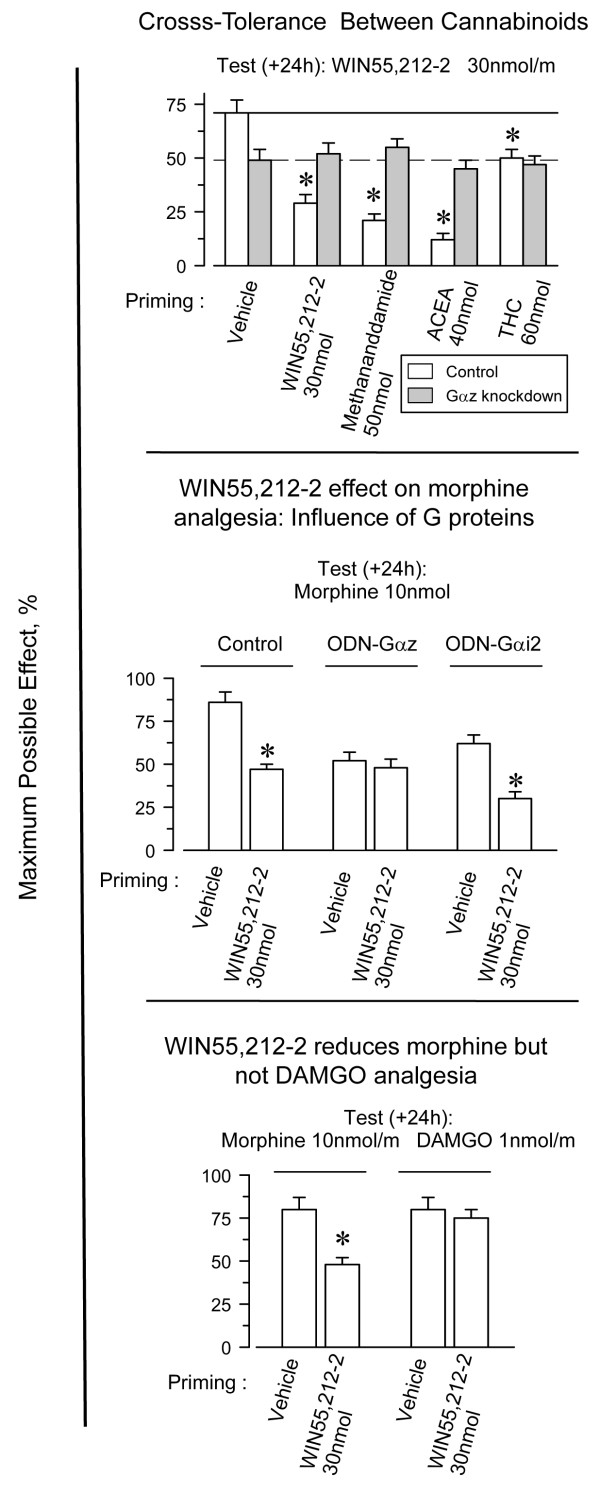
Figure 6.
Role of Gz proteins in the ability of WIN55,212-2 to reduce morphine analgesia. Upper panel: Cross-tolerance between CB1R agonists in wild type and Gαz knockdown mice. A priming dose of WIN55,212-2 (icv; 30 nmol) was administered to the mice, and their response to WIN55,212-2, methanandamide, ACEA or THC was evaluated 24 h later. Values are mean ± SEM from groups of eight mice. *Significantly different from the control group injected with the vehicle instead of the priming dose of WIN55,212-2 and also receiving the test dose of this agonist (P < 0.05). Middle panel: WIN55,212-2 does not reduce morphine analgesia in mice showing reduced expression of Gαz subunits. The activity of WIN55,212-2 on morphine-evoked antinociception was studied in mice showing reduced expression of either Gαi2 or Gαz subunits. *Significantly different from the control group injected with the vehicle instead of the priming dose of WIN55,212-2 (P < 0.05). Lower panel: Effect of WIN55,212-2 on MOR-mediated analgesia. A priming dose of WIN55,212-2 (icv; 30 nmol) was administered to mice 24 h before testing the supraspinal analgesic response to morphine and DAMGO. Control mice received vehicle instead of the cannabinoid agonist. *Morphine displays significantly lower analgesic effect on mice that previously received WIN55,212-2 instead of vehicle (P < 0.05).