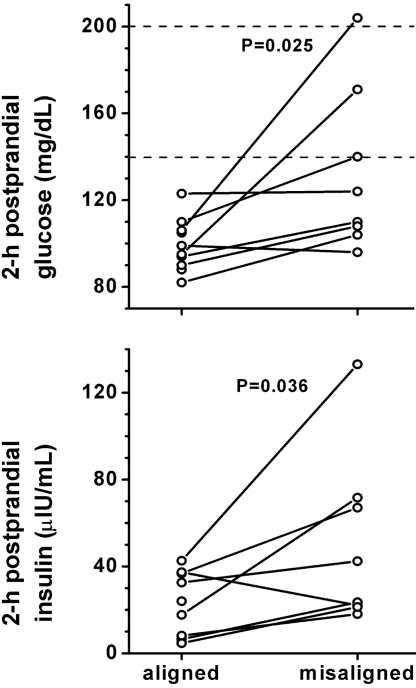
Fig. 5.
Circadian misalignment reduces glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. During circadian misalignment, 2-h postprandial glucose (Top panel) and insulin (Bottom panel) levels were significantly increased as compared to normal alignment. Dotted lines, 140 mg/dL and 200 mg/dL 2-h postprandial glucose, above which levels are considered prediabetic and diabetic, respectively; P-values, statistical significance for effect of misalignment.