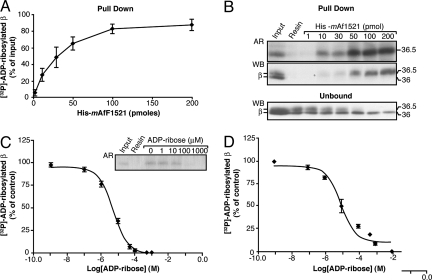
Fig. 2.
Efficiency and reversibility of binding to His6-mAf1521 of the ADP-ribosylated βγ dimer. CHO plasma membrane proteins (10 μg) and 250 ng of purified βγ dimer were ADP-ribosylated in the presence of [32P]-NAD+ for 12 h at 30°C. After solubilization, they were pulled down with His6-mAf1521. (A) Increasing concentrations of His6-mAf1521 in the [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit pull-down assay, shown as percentage of the input of [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit (≈4 pmol). Data are means ± SD of five independent experiments. (B) As for (A), showing pulled-down samples and unbound fractions (one-eighth of the total volume) from a representative experiment, as analyzed by autoradiography (AR) and by Western blotting (WB) with an antibody against the β subunit that recognizes both the unmodified (36 kDa) and the ADP-ribosylated (36.5 kDa) β subunit. The disappearance of the [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit from the unbound fraction was also followed in parallel (B, lower). (C) Pull-down of the [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit after its incubation with 30 pmol of His6-mAf1521 in the presence of increasing concentrations of ADP-ribose (1 nM to 1 mM) (“competition” conditions). Data are expressed as percentages of [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit pulled down in the absence of ADP-ribose and are means ± SD from three independent experiments. Inset: Autoradiography of the pulled-down samples from a representative experiment. (D) As for (C), but with the addition of ADP-ribose after the pull-down assay of the [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit by 30 pmol of His6-mAf1521 (“displacement” conditions). At 100 μM ADP-ribose (≈400 pmol under these incubation conditions), all of the His6-mAf1521-bound [32P]-ADP-ribosylated β subunit (≈4 pmol) was displaced. A ≈100-fold excess of ADP-ribose can displace the immobilized ADP-ribosylated β subunit from the His6-mAf1521-resin complex. Data are means ± SD from three independent experiments. Curve fitting analyses in (C) and (D) were performed with GraphPad PRISM, giving ADP-ribose EC50 values of 5 and 10 μM, respectively.