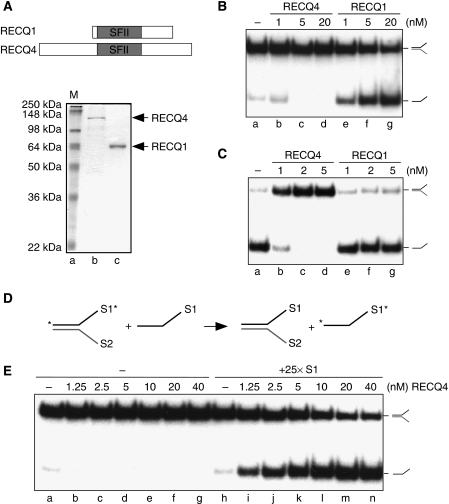
Figure 1.
Biochemical activities of human RECQ4. (A) (Upper) Schematic diagram of RECQ1 and RECQ4 helicases. The conserved SFII helicase domain is shown in grey. (Lower) Visualization of recombinant RECQ1 and RECQ4 proteins purified from E. coli by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (B) Helicase activities of the recombinant RECQ1 and RECQ4 proteins. Dissociations of the 32P-labelled splayed-arm structures were carried out using indicated amounts of proteins. 32P-Labelled single-stranded DNA products were visualized by autoradiography following neutral PAGE. (C) DNA strand annealing activities of the recombinant RECQ1 and RECQ4 proteins. DNA annealing of 32P-labelled S1 and unlabelled complementary S2 oligos were carried out using the indicated amounts of proteins. The annealed 32P-labelled splayed-arm products were visualized as described in (B). (D) Scheme of DNA helicase assay in the presence of excess of unlabelled S1 oligos. DNA unwinding allows the separation of 32P-labelled S1 (indicated with an asterisk) and unlabelled S2 to ssDNA. DNA annealing promotes the hybridization between the excess amounts of unlabelled S1 with S2, allowing the stabilization of the single-stranded 32P-labelled S1. (E) Helicase activities of the recombinant RECQ4 in the presence and absence of unlabelled S1 oligos. 32P-Labelled dissociated products were visualized by autoradiography following neutral PAGE.