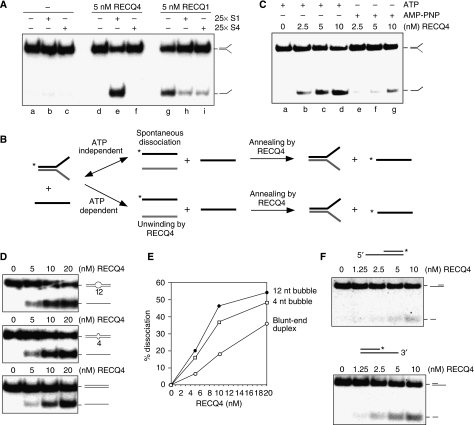
Figure 2.
ATP-dependent DNA unwinding activity of human RECQ4. (A) Comparison of the helicase activities of the recombinant RECQ4 and RECQ1 in the presence of unlabelled S1 or a control oligo, S4, with different sequence composition. (B) Schematic diagram of the production of 32P-labelled single-stranded S1 in the DNA dissociation reaction. 32P-end labels are indicated with asterisks. In the ATP-independent event (upper), low level of spontaneous DNA dissociation of splayed arm allows the exchange of 32P-labelled single-stranded S1 with the unlabelled S1, a reaction facilitated by the DNA annealing activity of RECQ4. In the ATP-dependent reaction (lower), DNA dissociation is catalysed by RECQ4 unwinding of splayed arm upon ATP hydrolysis to generate 32P-labelled single-stranded S1, which is then stabilized by the presence of unlabelled S1 to compete for re-annealing back to S2. (C) Helicase activities of the recombinant RECQ4 using splay-arm substrates in the presence of ATP or AMP-PNP. (D) Helicase assays of the recombinant RECQ4 proteins were carried out as described using duplex DNA with 12-nt bubble (upper panel), duplex DNA with 4-nt bubble (middle panel) and blunt-ended duplex DNA (lower panel). (E) Product formation in (D) was quantified by phosphorimaging. Close circle, dissociation product using duplex DNA with 12-nt bubble. Open rectangle, dissociation product using duplex DNA with 4-nt bubble. Open circle, dissociation product using blunt-ended duplex DNA. (F) Helicase activities of the recombinant RECQ4 using either a 32P-labelled 5′ overhang (upper panel) or 3′ single stranded overhang (lower panel).