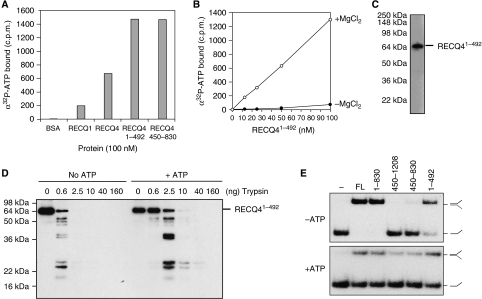
Figure 4.
Novel ATP-binding domain of the RECQ4 N terminus. (A) Spin-column analysis of the binding of α32P-ATP by the indicated protein. Following centrifugation, the α32P-ATP present in the flow through or void volume indicates the amount bound by the indicated protein. (B) Spin-column analysis of the binding of α32P-ATP by the indicated amounts of RECQ41–492 in the presence (open circle) or absence (close circle) of MgCl2. (C) Visualization of RECQ41–492 fragment binding to α32P-8-azido-ATP after UV crosslinking by autoradiography following SDS–PAGE. (D) Trypsin proteolysis mapping of RECQ41–492 in the presence or absence of ATP. Protein fragments were separated on SDS–PAGE followed by western blot analysis using anti-FLAG antibody. (E) DNA strand annealing activities of the RECQ4 full length (FL) and fragments (5 nM each). DNA annealing of 32P-labelled S1 and unlabelled complementary S2 oligos were carried out using the indicated proteins without ATP (upper panel) or in the presence of ATP (lower panel).