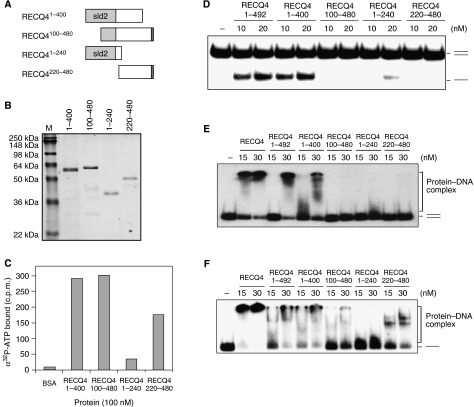
Figure 5.
Biochemical analysis of the RECQ4 N-terminal domain. (A) Schematic diagram of the N-terminal fragments. The amino-acid residues covered by each of the fragments are indicated, and the Sld2-like domain is shown in light grey. (B) Visualization of recombinant N fragments purified from E. coli by SDS–PAGE and Commassie blue staining. (C) Spin-column analysis of the binding of α32P-ATP by the indicated N-terminal fragments. (D) Helicase activities of different RECQ4 N-terminal fragments using duplex DNA. (E) Binding of 32P-end-labelled duplex oligos by RECQ4 full length and different RECQ4 N-terminal fragments. DNA–protein complex was analysed on 5% native PAGE. (F) Binding of 32P-end-labelled single-stranded oligos by RECQ4 full length and different RECQ4 N-terminal fragments. DNA–protein complex was analysed on 5% native PAGE.