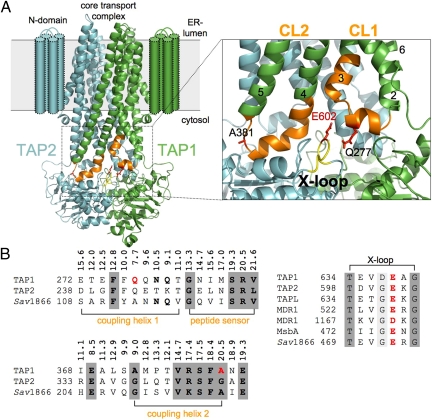
Fig. 1.
The TMD–NBD interface of the TAP complex. (A) Three-dimensional homology model of the core TAP complex composed of TAP1 (green) and TAP2 (cyan) based on the x-ray structure of Sav1866 (PDB ID code 2HYD) (22). Cylinders indicate the TM helices of the extra N domain. CL1 and CL2 are extensions between TM2 and TM3 and between TM4 and TM5, respectively. The region of CL1 and CL2 in TAP1 investigated by cysteine-scanning and cross-linking is colored orange, and the X-loop of TAP2 is colored yellow. The conserved glutamate (E602) in the X-loop and residues in CL1 and CL2 (Q277 and A381) are highlighted in red using a stick representation. A magnification of the transmission interface illustrates the close interaction of coupling helices 1 and 2 with the X-loop of TAP2. TM helices are indicated by numbers. (B) The multiple alignments of the transmission interface of different ABC exporters [UniProt accession numbers: Q03518/9, human TAP1/2 (ABCB2/3); Q9NP78, human TAPL (ABCB9); P08183, human MDL1 (ABCB1); P63359, S. typhimurium MsbA; and Q99T13, S. aureus Sav1866] derived by using ClustalW2 is shown. Coupling helices 1 and 2, the peptide sensor, and the X-loop are presented. Based on the 3D homology model, Cα distances between residues of CL1 and CL2 and E602 (X-loop) are derived. E602 (X-loop), Q277 (CL1), and A381 (CL2) are labeled in red. Residues with significant and high conservation are bold and shaded dark gray, respectively.