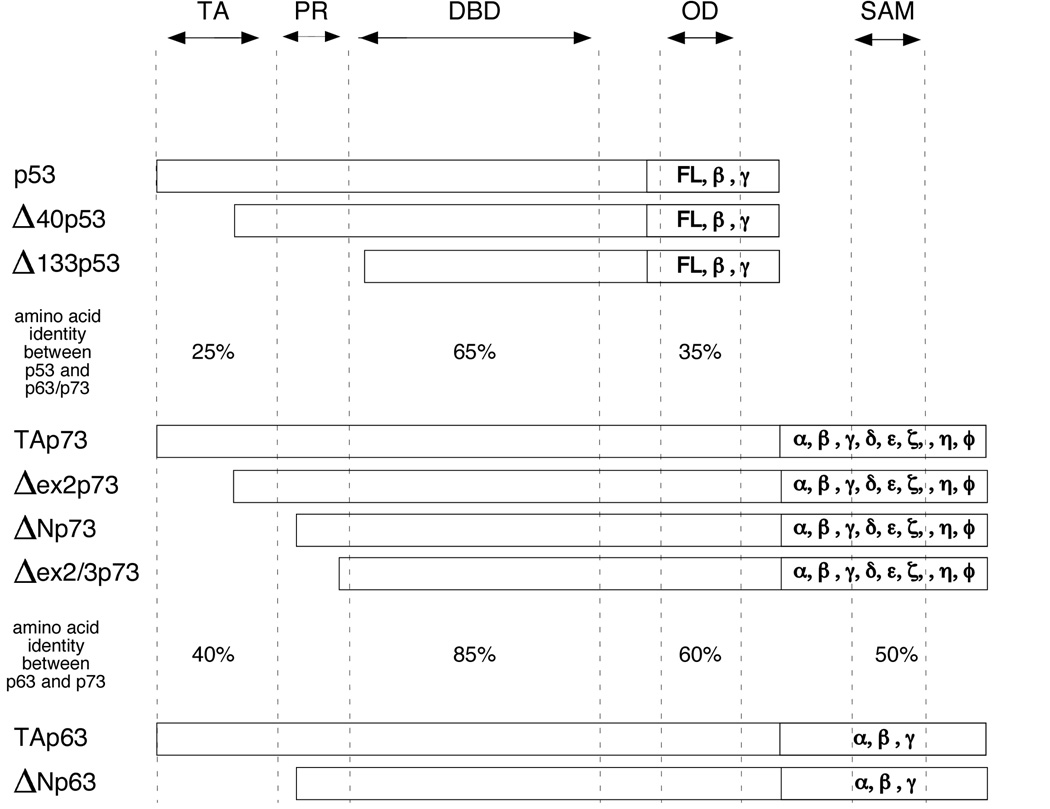
Figure 1. p53 family member isoforms.
Schematic presentation of p53, p63, and p73 isoforms. Approximate location of the transactivation (TA) domain, proline rich domain (PR), DNA binding domain (DBD), oligomerization domain (OD) and the sterile alpha motif (SAM) are indicated. The amino acid identity between the TA, DBD, and OD of p53 and p63/p73 as well as between p63 and p73 is denoted. Full length (FL) p53 or TAp63 and TAp73 protein are transcribed from a promoter located in the non-coding region of exon 1 (P1 promoter) of the p53, p63, and p73 gene. Δ133p53, ΔNp63, and ΔNp73 isoforms are generated by transcription from a promoter (P2 promoter) located in intron 3 of the p63 and p73 gene or intron 4 of the p53 gene. Further ΔN variants are generated by alternative splicing of the N-terminus (Δ40p53, Δex2p73, Δex2/3p73). Alternative splicing of the C-terminal region yields additional variants for p53 (FL, β, & γ), p63 (α, β, & γ), and p73(α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η, & θ). p53 β and γ lack the oligomerization domain.