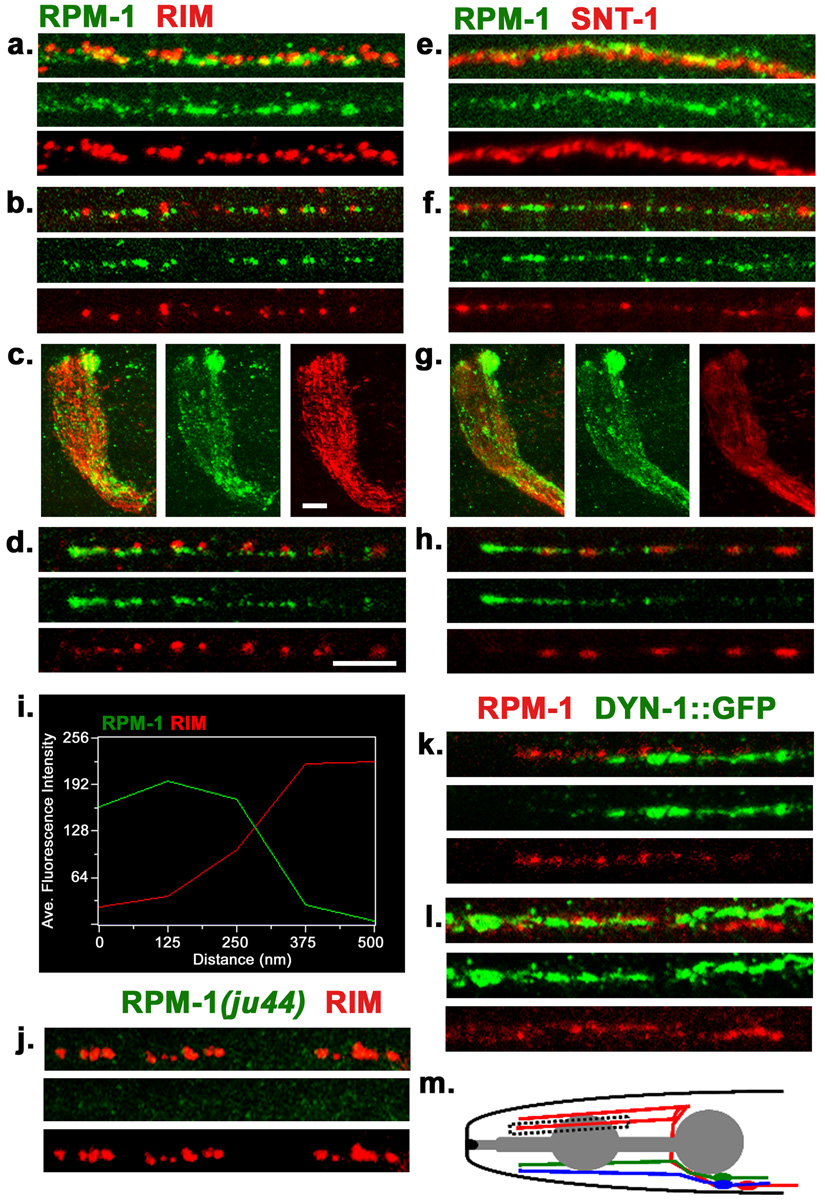
Figure 1. Endogenous localization of RPM-1.
(a–d) Confocal images of wild type (N2) worms co-stained with anti-RPM-1 (green) and anti-RIM (red) in (a) dorsal cord, (b) sub-lateral cord, (c) nerve ring, (d) SAB neuron. (e–h) Confocal images of N2 worms co-stained with RPM-1 (green) and synaptotagmin/SNT-1 (red) in (e) dorsal cord, (f) sub-lateral cord, (g) nerve ring, (h) SAB neuron. (i) Fluorescence intensity plot showing the typical distance between RPM-1 puncta and RIM in the dorsal cord. (j) The RPM-1 antibody is specific. Confocal images of the dorsal cord of rpm-1(ju44) mutants. RIM stain (red) is positive and shows gaps that are characteristics of the Rpm-1 mutant phenotype, whereas no RPM-1 staining is detected. (k–l) juIs83 (DYNAMIN-1::GFP) worms co-stained with RPM-1(red) and GFP (green) in (k) SAB neuron and (l) dorsal cord. (m) Schematic drawing of the SAB neurons. Blue, SABVL; green, SABVR; red, SABD. All SABs have their cell bodies in the retro-vesicular ganglion, project axons towards the anterior, and form en passant synapses onto head muscles. Box indicates region of SAB shown in d and h. All SAB images shown are in the same orientation with the anterior end on the left, individual SAB processes were chosen at random. Scale bars: 5µm, a, b, d, e, f, h, k, l, j . Scale bar, 10µm c, g,