Fig. 5.
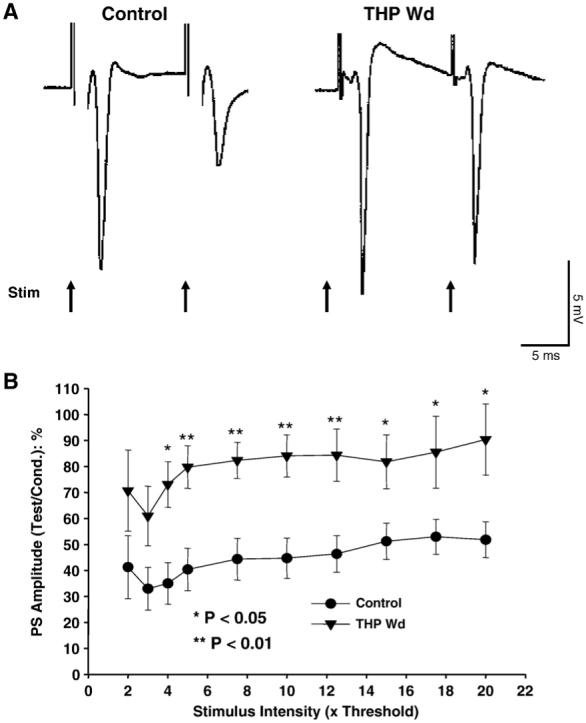
THP withdrawal reduces paired-pulse inhibition. Following 24 hr withdrawal from chronically administered THP (10 mg/kg, i.p. for 3 weeks) to adult, female rats hippocampal slices were prepared, and population EPSPs recorded from the pyramidal cell layer of CA 1 hippocampus in response to 2 stimulating pulses (4× threshold, 10 ms interpulse interval) delivered to the Schaffer collaterals. In contrast to the vehicle-injected controls, which exhibited a highly significant reduction in population spike amplitude in response to the second (test) pulse compared to the first (conditioning) pulse, reduction in PS amplitude in response to the second stimulus was not significantly different from the response to the first stimulus after THP withdrawal. This demonstrates a decrease in feedback inhibition after THP withdrawal. (A) Representative traces. (B) Population data (n = 10-12 slices/group).
