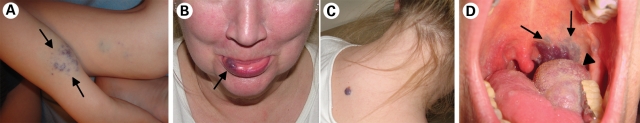
Figure 2.
The many faces of venous anomalies. Identification of their genetic bases has helped distinguish between (A) GVM, caused by loss-of-function of glomulin (GLMN), (B and C) VMCM, caused by inherited gain-of-function changes in TIE2/TEK, and (D) sporadic venous malformations, caused by somatic gain-of-function mutations in TIE2/TEK.