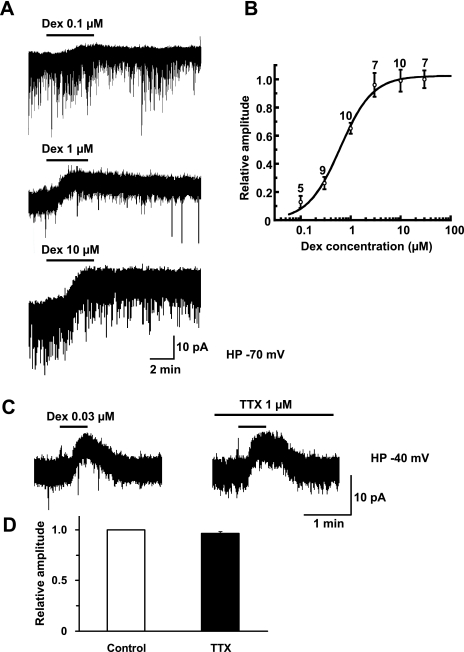
Fig. 1.
Dexmedetomidine induces an outward current in a concentration-dependent manner in SG neurons. (A) Outward currents induced by dexmedetomidine (0.1, 1 and 10 μm). Duration of drug superfusion is shown by horizontal bars above chart recordings. Holding potential = −70 mV. (B) Relative peak amplitude was calculated as an amplitude of the dexmedetomidine (0.1–30 μm)-induced current divided by that of the current produced by dexmedetomidine (30 μm). The continuous curve was drawn according to the Hill plot with an EC50 value of 0.62 μm (95% confidence interval, 0.51–0.77 μm) and a Hill coefficient of 1.34. The number next to each point denotes the number of neurons examined. Holding potential = −70 mV. (C) Outward currents elicited by dexmedetomidine (0.03 μm) in the absence and presence of TTX (1 μm). These currents were obtained from the same neuron (n= 5). Holding potential = −40 mV. (D) Relative peak amplitude was calculated as an amplitude of dexmedetomidine-induced current in the presence of TTX (5.3 ± 1.3 pA) divided by that of currents produced by dexmedetomidine (5.6 ± 1.4 pA) without TTX.