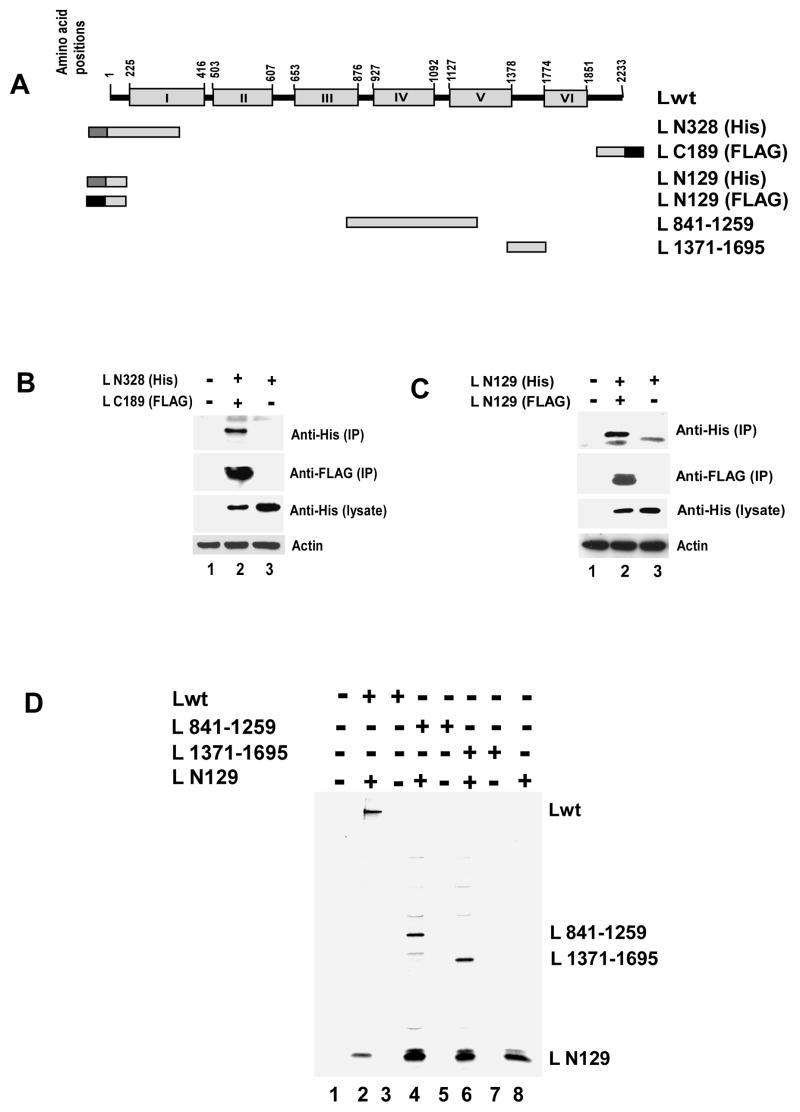
Fig 3.
(A) Schematic representation (not to the scale) of Lwt and deletion mutants. (B) Analysis of L-L interaction by co-immunoprecipitation assay. C-terrminally FLAG-tagged C-terminal 189 amino acids (L C189) were expressed together with N-terminally His tagged N-terminal 328 amino acids (L N328). Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG antibody coated beads. Western blot analyses were carried out using anti-His or anti-FLAG monoclonal antibodies for immunoprecipitated (IP) as well as total proteins (lysate). L N328 was co-immunoprecipitated with L C189 (lane 2 in upper and second panel from top). Similar level of expression of L N328 was confirmed in lysates (lane 2 and 3 in third panel from top) and anti-β actin antibody was used to verify the loading control (lower panel) (C) N- terminal 129 amino acids (L N129) were differentially tagged (His or FLAG) and co-expressed in HeLa cells. Lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitation was carried out using anti-FLAG antibody coated beads. Western blot analysis with anti-His and anti-FLAG antibody showed that L N129 self interacts (lane 2, top panel and second panel from top). His tagged L N129 was expressed at similar level in lysates (lane 2 and 3 in third panel from top) and synthesis of actin was used as loading control (lower panel) (D) FLAG-tagged L N129 was co-expressed with L 841-1259 or L 1371-1695. Proteins were labeled with 35S as described in text. Analysis of L-L interaction by co-immunoprecipitation assay showed L N129 efficiently interacts with both the L fragments.