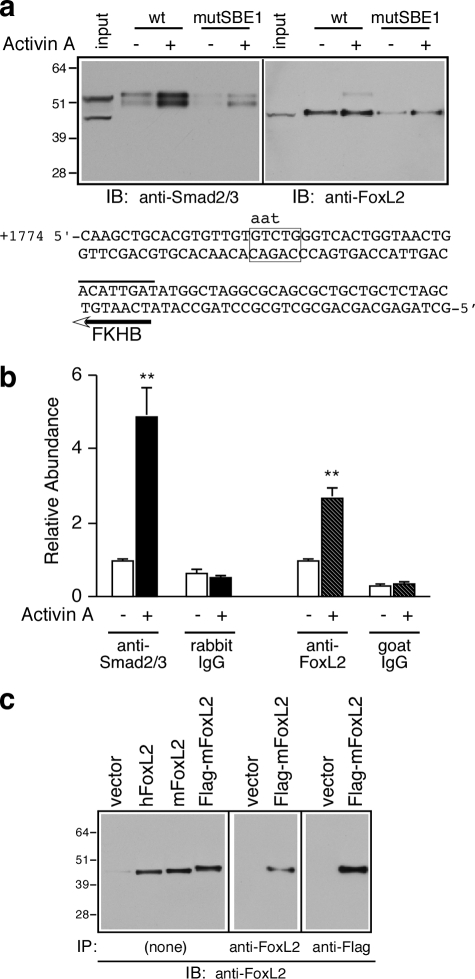
FIGURE 5.
Activin A induces the recruitment of Smad2/3 and FoxL2 to the intronic SBE1 of follistatin. a, oligonucleotide precipitation experiments utilized extracts of αT3-1 cells treated with vehicle or 1 nm activin A for 30 min. The cell extracts were precipitated with wild type (wt) or mutant (mutSBE1) SBE1 double-stranded biotinylated probes and subjected to Western blot analysis with either rabbit anti-Smad2/3 (left panel) or goat anti-FoxL2 (right panel) IgGs. The numbers to the left of the immunoblots (IB) correspond to protein size markers (kDa). The nucleotide sequence corresponds to the double-stranded biotinylated probe used for these experiments. The sequence shows the wild type SBE1 site (boxed) and the corresponding mutant form (indicated by lowercase letters) as well as the FKHB (marked by a line above and an arrow below the sequence). b, αT3-1 cells were treated with vehicle or activin A (1 nm for 30 min) and subjected to ChIP analysis using rabbit anti-Smad2/3, goat anti-FoxL2, or the corresponding normal rabbit or goat IgGs. The samples were then analyzed by real time PCR using a primer set surrounding the intronic SBE1 site of the endogenous mouse Fst or a primer set that amplifies a fragment located 5 kb upstream of the follistatin transcription start site. Real time PCR results (mean ± S.E. of triplicate determinations) of a representative experiment were calculated using the ΔΔCt method (**, p < 0.001 relative to the corresponding basal). c, protein extracts prepared from αT3-1 cells transfected with appropriate plasmids to express human FoxL2 (hFoxL2), mouse FoxL2 (mFoxL2), FLAG-tagged mFoxL2, or vector only were directly resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blot analysis (15 μg/lane; left panel). Alternatively, FLAG-mFoxL2 was first immunoprecipitated (IP) from αT3-1 extracts (200 μg) by incubation with either goat anti-FoxL2 (middle panel) or agarose-coupled mAb anti-FLAG (right panel) and then subjected to Western blot analysis using goat anti-FoxL2.