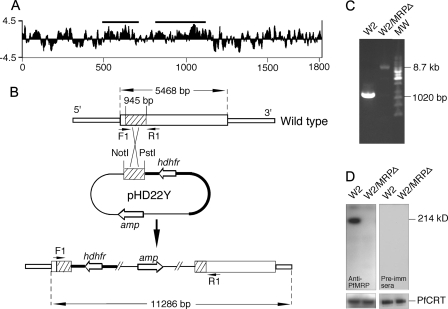
FIGURE 1.
Genetic knock-out of PfMRP in W2 P. falciparum parasite. A, Kyte_Doolittle hydrophilicity plot of the predicted amino acid sequence of PfMRP, showing two regions (horizontal bars) used in DNA vaccination to generate antibodies against PfMRP. The x axis is amino acid position, and the y axis is the hydrophilicity score. B, diagram showing a plasmid construct used to disrupt the gene encoding PfMRP. hdhfr is the gene encoding human dihydrofolate reductase, and amp is the gene encoding ampicillin resistance protein. The arrowheads (F1 and R1) indicate PCR primer positions before and after integration of the plasmid into chromosome. Restriction sites and predicted PCR product sizes are as marked. C, PCR products amplified from wild type W2 and W2/MRPΔ parasites using primers F1 and R1 in B. MW, molecular weight markers. The sizes of the PCR products were as expected from DNA sequences with or without plasmid integration, respectively. D, Western blot showing a 214-kDa band in W2 but not in W2/MRPΔ using mouse anti-PfMRP antibodies; no bands were detected in both W2 and W2/MRPΔ using mouse preimmune sera. Anti-PfCRT was used as loading control.