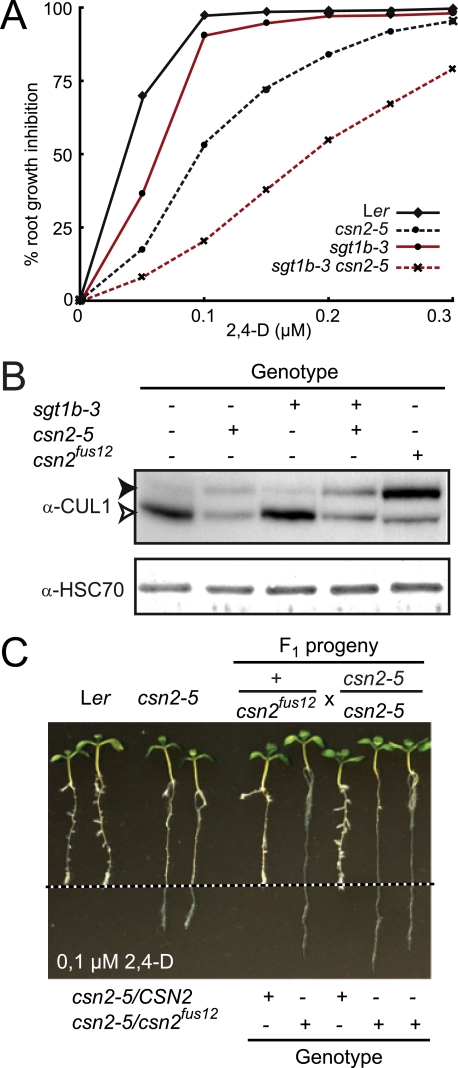
FIGURE 1.
Isolation and characterization of a hypomorphic csn2 mutant. A, inhibition of root elongation by increasing concentrations of synthetic auxin 2,4-D. Data points are averages of at least 10 seedlings, and standard deviations were less than 10%. Measurements of root elongation were performed on 8-day-old seedlings 3 days after transfer on auxin-containing medium. One representative experiment of four repetitions is shown. B, immunoblot analysis of total protein extracts with anti-CUL1 and anti-HSC70 antibodies. Immunodetection of cytosolic/nuclear HSC70 is used as loading control. Open and filled arrowheads correspond to unmodified and RUB-modified CUL1, respectively. + and -, indicate the presence and absence of sgt1b-3 and csn2-5 mutations, respectively. C, allelism test between Ler csn2-5 and Ler csn2fus12 mutants. Plants heterozygous for csn2fus12 were crossed to a homozygous csn2-5 mutant. F1 progeny were analyzed in the root growth inhibition assay on 0.1 μm 2,4-D as described in A. The dashed line indicates the position of the root tip immediately after transfer. F1 seedling genotypes at the CSN2 locus are indicated as determined using allele-specific PCR markers.