Fig. 4.
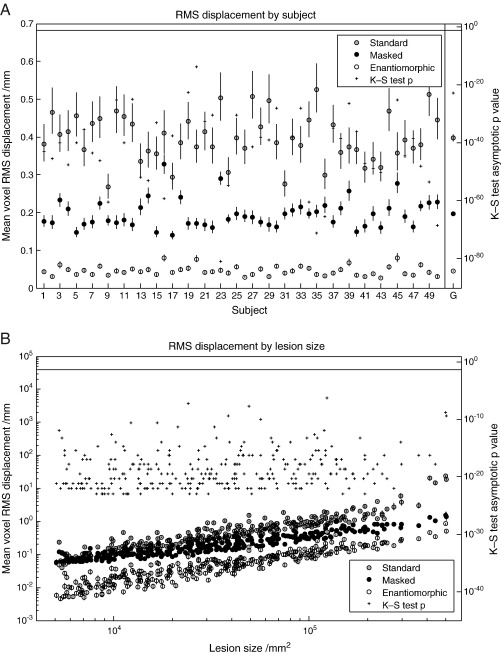
(A) RMS displacement by subject (T2 dataset with zero-filled lesions). The left hand axis shows whole brain mean voxel RMS displacement (the difference between the deformation fields describing the normalization of lesioned and unlesioned versions of the same image) with standard errors, plotted by individual subjects. The means include all 305 lesions and were derived – owing to log normality – by first log transforming the data, calculating the means and standard errors and anti-logging the results. The right hand side shows the asymptotic p values from a one-tailed, two sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test carried out on the untransformed data from the masked and the enantiomorphic methods. The vertical line at the top defines the 0.05 significance level. The values in the far right column represent the group means and associated standard errors. The corresponding p value was derived from an appropriate Kolmogorov–Smirnov test on the group means. (B) RMS displacement by lesion size (T2 dataset with zero-filled lesions). The left hand axis shows whole brain mean voxel RMS displacement with standard errors, plotted by lesions size. The means include all 50 subjects and were derived – owing to log normality – by first log transforming the data, calculating the means and standard errors and anti-logging the results. The right hand side shows the asymptotic p values from a one-tailed, two sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test carried out on the untransformed data from the masked and the enantiomorphic methods. The vertical line at the top defines the 0.05 significance level.