Abstract
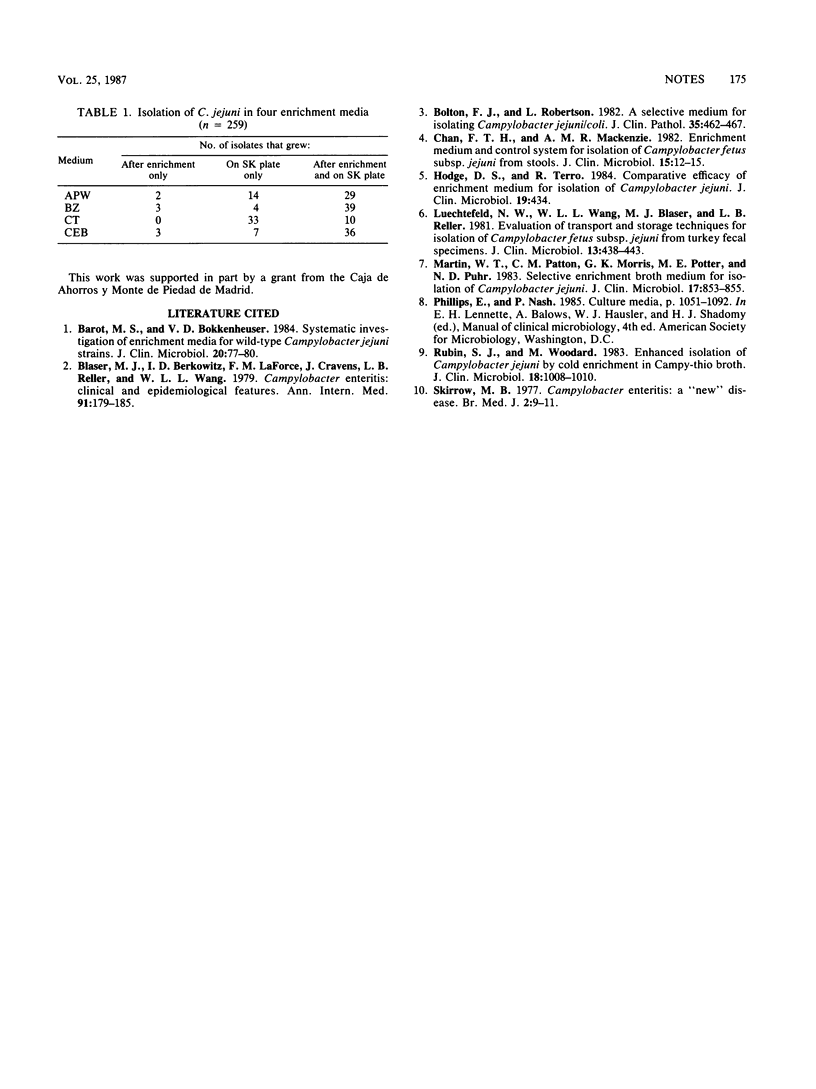
Diarrheal stool specimens were inoculated into the following media: alkaline peptone water (APW), Bruce-Zochowsky medium (BZ), Campylobacter enrichment broth (CEB), Campy-thio broth (CT), and Skirrow blood-agar (SK) plate. All media were incubated at 42 degrees C in microaerophilic conditions for 24 h. Afterwards, a new SK plate was inoculated from every liquid medium. Campylobacter jejuni was isolated from 43 of the 259 specimens when CT was used, from 45 when APW was used, from 46 when BZ was used, and from 46 when CEB was used; these totals include specimens that grew after enrichment only, on SK plates only, and both after enrichment and on SK plates. No significant differences were found between the isolates obtained with and without enrichment procedures.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barot M. S., Bokkenheuser V. D. Systematic investigation of enrichment media for wild-type Campylobacter jejuni strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):77–80. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.77-80.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Robertson L. A selective medium for isolating Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Apr;35(4):462–467. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan F. T., Mackenzie A. M. Enrichment medium and control system for isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from stools. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):12–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.12-15.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge D. S., Terro R. Comparative efficacy of liquid enrichment medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):434–434. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.434-.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luechtefeld N. W., Wang W. L., Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Evaluation of transport and storage techniques for isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from turkey cecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):438–443. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.438-443.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Morris G. K., Potter M. E., Puhr N. D. Selective enrichment broth medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):853–855. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.853-855.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Woodard M. Enhanced isolation of Campylobacter jejuni by cold enrichment in Campy-thio broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):1008–1010. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.1008-1010.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


