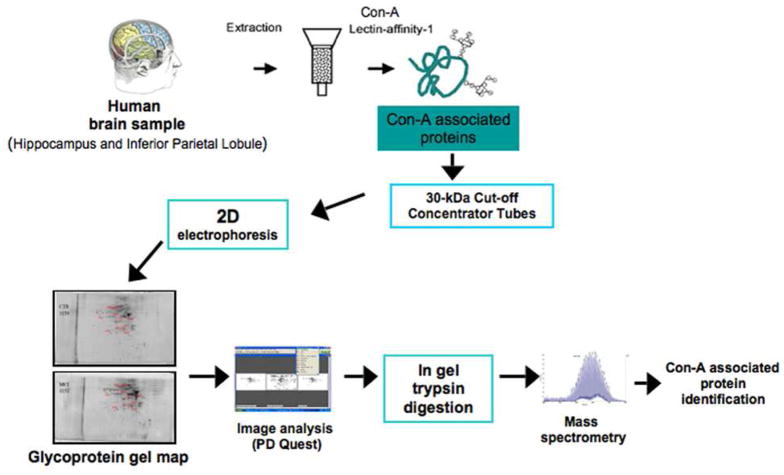
Figure 1.
Method Overview.
The use of Con-A lectin-affinity chromatography coupled to 2D electrophoresis allows the separation and the resolution of Con-A-associated proteins.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia, comprising 60–80% of all reported cases, and currently affects 5.2 million Americans. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) arguably is the earliest for of AD. The present study identifies Con-A-fractionated brain proteins AD and MCI in two brain regions. The identity of proteins with altered levels in AD and MCI brain are consistent with biochemical and/or pathological alterations in both disorders.