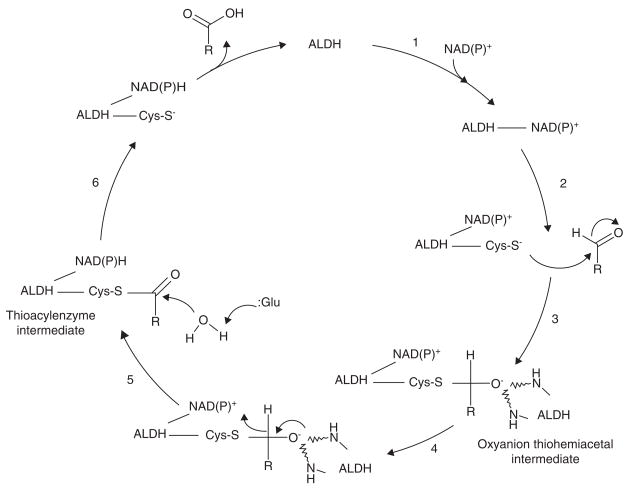
Figure 3. Proposed non-CoA dependent ALDH catalysis mechanism.
1, Cofactor binding results in a conformation change of the enzyme and activation of the catalytic thiol (Cys-S−); 2, Nucleophilic attack of the aldehyde substrate; 3, Oxyanion intermediate stabilized by two NH groups of the ALDH peptide chain; 4, Hydride transfer to cofactor. 5; Glutamate residue acts as a base catalyst in the hydrolysis of the thioacylenzyme intermediate; 6, Release of carboxylic acid product followed by cofactor.