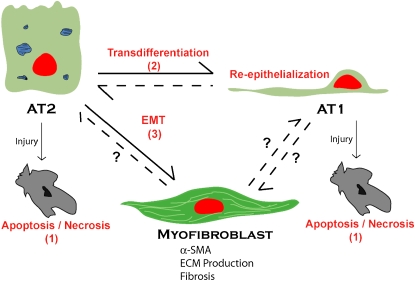
Figure 3.
Alveolar epithelial transdifferentiation pathways. AECs demonstrate a previously unappreciated pluripotency. Under normal conditions, alveolar type II (AT2) cells transdifferentiate into alveolar type I (AT1) cells. In vitro, AT1 cells can also transdifferentiate into AT2 cells. Depending on the cellular environment and stimuli, AECs respond to injury by traveling down one of a number of pathways: apoptosis/necrosis (1); proliferation, transdifferentiation, and re-epithelialization (2); or EMT (3) to a myofibroblast phenotype, resulting in extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, destruction of lung architecture, and fibrosis.