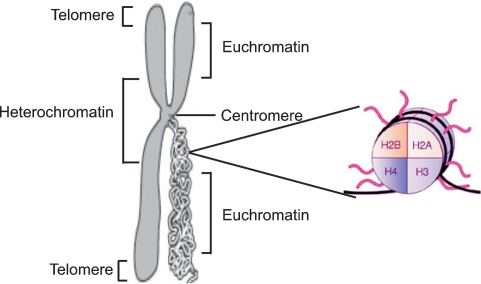
Fig. 1.
Schematic figure of chromatin and histone structure. Chromatin is the complex of DNA and protein that makes up chromosomes. Heterochromatin locates in the centromeric region and telomeres whereas transcritpionally active euchromatin is located in the less condensed region. The functions of chromatin are to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and to serve as a mechanism to control expression. The major proteins involved in chromatin are histone proteins. The flexible N-terminal tails of the four core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 may undergo a range of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, methylation, O-GlcNac modification, phosphorylation and ubiquitination, all leading to changes in the gene expression level.