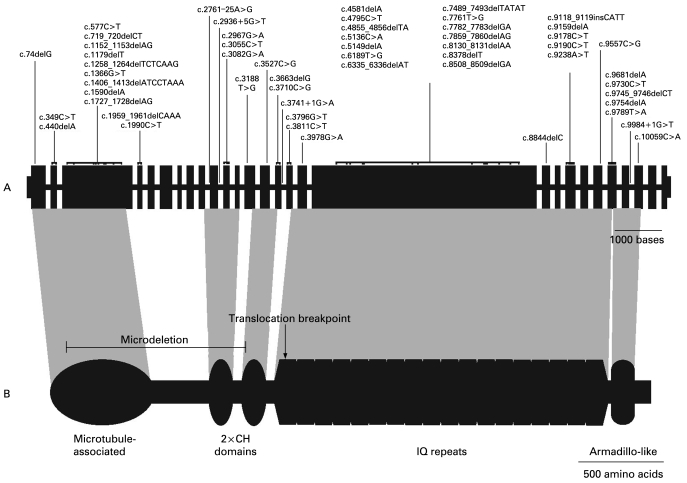
Figure 1.
ASPM gene, protein and sites of autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (MCPH) mutations. (A) The exon/intron structure of the ASPM gene. Exons are scaled relative to each other, with exon 18 being the largest at 4.7 kb. Introns vary significantly in size, but for clarity are all shown as having the same arbitrary size. The position of the reported mutations is indicated, with italicised text denoting splicing mutations. All mutations are detailed in table 1. (B) The known and predicted domains of the ASPM protein: a microtubule binding domain; two calponin homology (CH) domains which are possibly responsible for transportation of the ASPM protein to the spindle poles; a region of 81 IQ/calmodulin binding domains; and a conserved armadillo-like C-terminal domain of unknown significance. The regions of the ASPM protein affected by the previously reported translocation breakpoint (Pichon et al33) and the microdeletion first reported here are shown by an arrow and a bar, respectively.