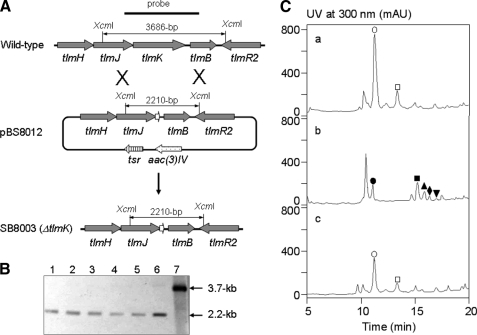
FIGURE 2.
Inactivation of tlmK and genetic complementation to the ΔtlmK in-frame deletion mutant. A, construction of the ΔtlmK mutant strain SB8003 and restriction maps of the S. hindustanus wild-type and SB8003 mutant strains as well as the pBS8012 cosmid carrying the ΔtlmK in-frame deletion mutation upon XcmI digestion. B, Southern analysis of the ΔtlmK mutant strain SB8003 (lanes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 for five independent isolates) with the ΔtlmK mutant construct pBS8012 (lane 6) and tlmK wild-type construct pBS8008 (lane 7) as controls upon XcmI digestion and using the 2.2-kilobase (kb) PCR-amplified fragment from the wild-type strain as a probe. C, HPLC analysis of (a) TLM production in S. hindustanus wild type, (b) new metabolite accumulation in the ΔtlmK mutant strain SB8003, and (c) restoration of TLM production in the ΔtlmK-complemented recombinant strain SB8004. ○, TLM A; □, TLM B; •, TLM K-1; ▪, TLM K-2; ▴, TLM K-3; ♦, TLM K-4; ▾, TLM K-5. mAU, milliabsorbance.