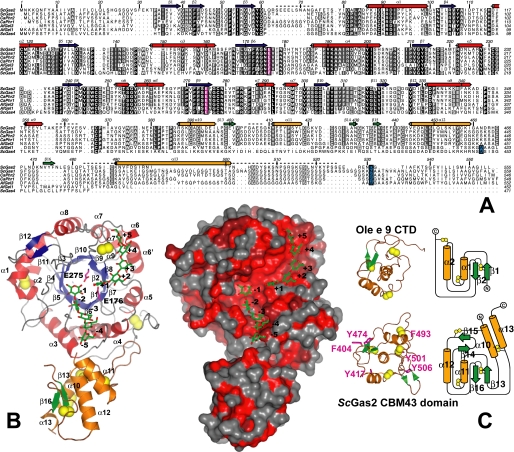
FIGURE 1.
Overall structure of ScGas2 and comparison with structurally related proteins. A, multiple sequence alignment of the GH72 family members ScGas2, ScGas1, CaPHR2, CaPHR1, AfGel3, AfGel1, and ScGas4. Secondary structure elements from the ScGas2 structure are shown, with α-helices in red and orange for the catalytic and cysteine-rich domains, respectively, and β-strands correspondingly in blue and green. Regions that are disordered in some or all of the ScGas2 structures are marked with a dashed line. Conserved catalytic glutamate residues are highlighted in pink boxing, and the (predicted) GPI-anchor attachment site is indicated in blue boxing. B, overall crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with laminaripentaose. The Glu176 and Glu275 are shown with pink carbon atoms and labeled. The seven disulfide bridges are highlighted in yellow. Helix α13 was not built in the laminaripentaose complex structure and thus is absent from this figure. Ligand molecules are shown as sticks with green carbon atoms and the sugar-binding sites are labeled –5 to +5, following standard nomenclature. Other colors as in A. Also shown is a surface representation of the ScGas2, colored by sequence conservation (red (100% identity) to gray (<50% identity)). C, comparison of the CBM43 domains of ScGas2 (bottom; E176Q mutant) and Ole e 9 (top; PDB ID 2JON (39)). Disulfide bridge sulfur atoms are shown as yellow spheres. Secondary structure elements are colored as in B and labeled. Unique features of either structure are shown in lighter colors in the picture (left). The topology diagram was drawn with Topdraw (50). Surface-exposed aromatic amino acids of the CBM43 domain of ScGas2 (Phe404, Tyr417, Tyr474, Phe493, Tyr501, and Tyr506) are shown as sticks with pink carbon atoms.