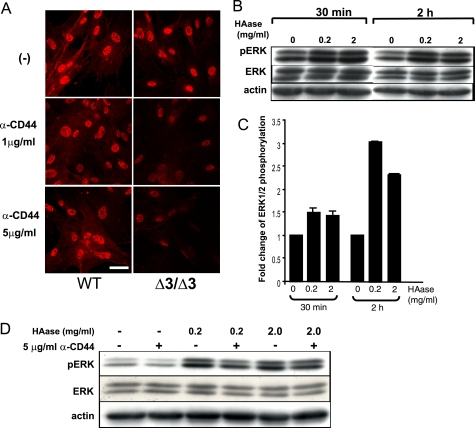
FIGURE 6.
Effects of hyaluronidase treatment and blocking of HA-CD44 interaction on phosphorylation of ERK1/2. A, effects of anti-CD44 treatment on phospho-ERK1/2. Immunostaining patterns for phospho-ERK1/2 are shown. Δ3/Δ3, the Cspg2Δ3/Δ3 fibroblasts. Both WT and the Cspg2Δ3/Δ3 fibroblasts were cultured in the presence of an anti-CD44 antibody that blocks HA-CD44 interaction at 1 or 5 μg/ml, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Note that treatment with the antibody substantially diminishes the staining intensity for phospho-ERK1/2 in the Cspg2Δ3/Δ3 fibroblasts (bar, 20 μm). B, effects of hyaluronidase treatment on phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in WT fibroblasts. The cells were treated for the periods at the concentrations of hyaluronidase (HAase) as indicated and applied to immunoblot analysis to detect phospho-ERK1/2 (pERK), total ERK1/2 (ERK), and actin. C, phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2. The band density was quantified using a densitometer. That of phospho-ERK1/2 standardized by that of total ERK1/2 is shown. D, effects of combined treatment with hyaluronidase and anti-CD44. The cells were treated with combinations of hyaluronidase and anti-CD44 (α-CD44) for 2 h at the concentrations indicated and applied to immunoblot analysis to detect phospho-ERK1/2 (pERK), total ERK1/2 (ERK), and actin.