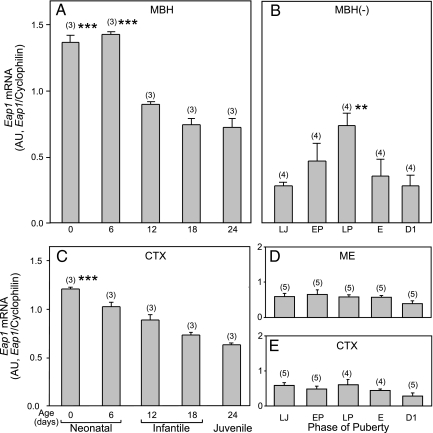
Figure 1.
Eap1 mRNA abundance changes in the rat hypothalamus during female sexual development, as assessed by semiquantitative PCR. A, Eap1 mRNA content decreases in the MBH between the end of the infantile period (PN d 6) and the first half of juvenile development (PN d 24). B, Eap1 expression in the MBH separated from the ME (MBH−) increases at the time of puberty reaching maximum values on the day of first proestrus (LP). C, Eap1 mRNA content in the CTX decreases steadily from the time of birth to the first half of the juvenile period. D, Eap1 mRNA content does not change in the ME at the time of puberty. E, Eap1 mRNA content remains at low levels in the CTX throughout puberty. The results are expressed as ratios between Eap1 and cyclophilin mRNA. AU, Arbitrary units; E, first estrus. Numbers in parentheses above bars indicate the number of animals per group, and vertical bars represent sem. ***, P < 0.01 vs. all older ages (A and C); **, P < 0.02 vs. all other groups, except EP (ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test) (B).