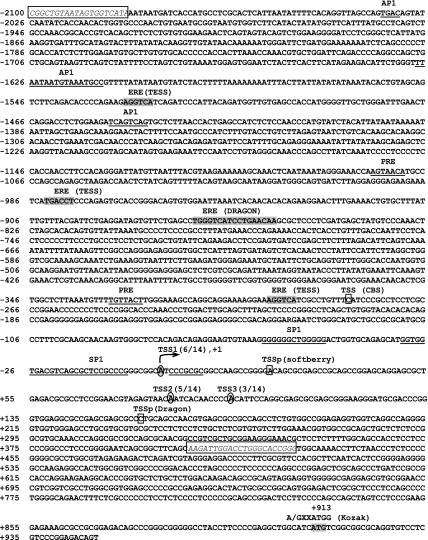
Figure 3.
The 5′-flanking region of the rEap1 gene. Based on the human EAP1 gene sequence, the homologous rat sequence was identified, and a 2-kb upstream region was analyzed in silico for potential TSSs (denoted by squares; the online tools used to predict TSSs are shown in parentheses) and transcription factor binding sites (underlined sequences). A search for EREs was performed using the Dragon Promoter Finder and TESS search webtools (gray highlights, names of web tools in parentheses). Experimental identification of rEap1 TSSs by RACE PCR identified three TSSs (shown by letters inside ovals). All three sites are located within a 100-bp range. The most frequent site, detected in six of 14 clones, was termed TSS1 and was given the position +1. The second most frequently used TSS (five of 14 clones) was termed TSS2, and the third most frequently used TSS (three of 14 clones) was termed TSS3. A fragment containing 2100 bp of DNA upstream from TSS1 and 429 bp of 5′-untranslated mRNA sequence was then PCR amplified using specific primers (framed sequences in italics) and subcloned into the pGL3-Basic luciferase vector.