Figure 5. Induction with β-naphthoflavone causes recombination in the liver, leading to conditional loss of Chk1 expression.
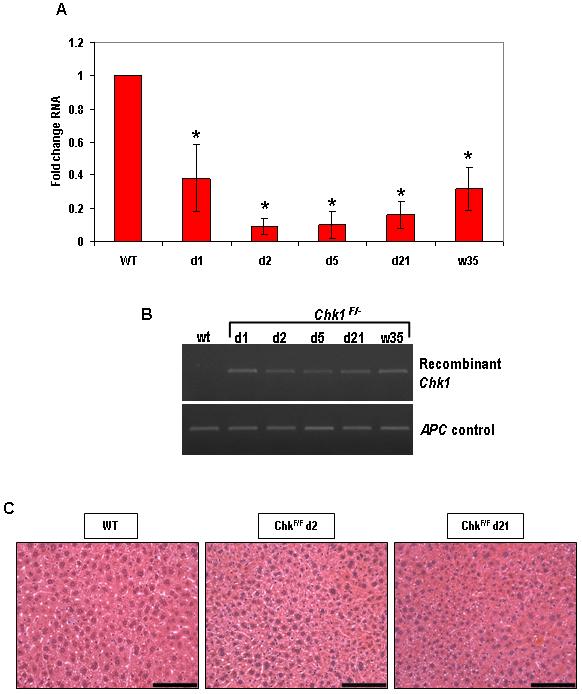
Cre activity was induced in wild-type (AhCre+Chk1+/+) and experimental (AhCre+Chk1F/F) by 3 consecutive i.p. injections of 80mg/kg β-naphthoflavone in 24h. Animals were culled at various time-points (day 1 to day 21) after induction and tissue was isolated from both control and experimental animals. (A) Loss of Chk1 RNA expression from the liver was determined by qRT-PCR. The PCR was carried out using primers designed to detect transcript from the deleted exon 2 of Chk1 (see Materials and Methods) and the data shown is in terms of fold-change of the Chk1/β-actin ratio compared to AhCre+Chk1+/+. *, P < 0.05. (B) Recombination in the liver was confirmed by semi-quantitative PCR using primers designed to detect the recombined Chk1 allele. DNA was isolated from tissue harvested from Cre-induced wild-type and experimental animals and detection of the recombined allele yielded a 436 bp product. Primers against the wild-type APC allele were used as a control. (C) H&E-stained histological sections of mouse liver from AhCre+Chk1F/F mice at various timepoints (day 2 and day 21) PI demonstrates no change in histology when compared to wild-type (AhCre+Chk1+/+).
