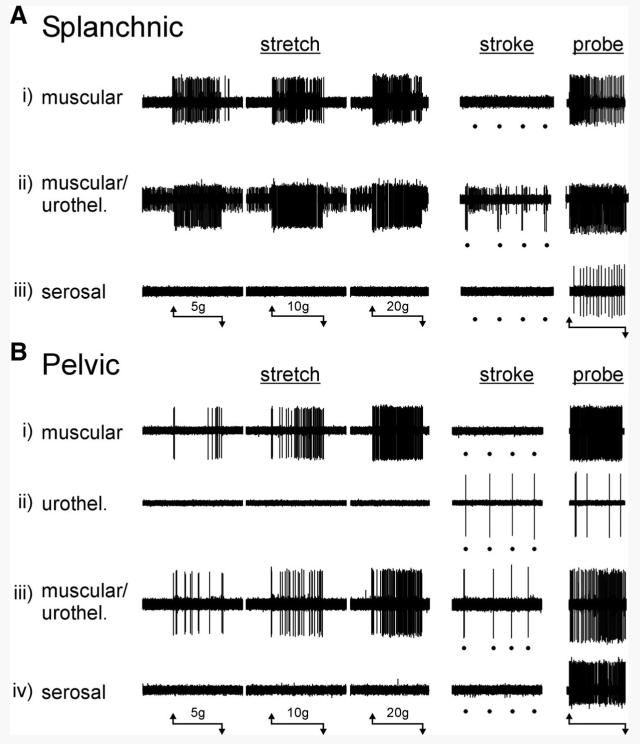
FIG. 1.
Types of mouse urinary bladder afferent fibers classified on the basis of responses to mechanical stimuli. A: 3 types of mechanosensitive fibers were identified in the lumbar splanchnic pathway: i) muscular afferents were activated by stretch and von Frey probing, but not by urothelial stroking (10 mg); ii) muscular/urothelial fibers were activated by stretch, urothelial stroking, and von Frey probing; iii) serosal afferents were activated only by von Frey probing and not by either stretch or urothelial stroking. B: 4 types of mechanosensitive fibers were identified in the pelvic pathway: i) muscular afferents were activated by stretch and von Frey probing, but not by urothelial stroking (10 mg); ii) urothelial afferents were activated by urothelial stroking (10 mg) and von Frey probing, but not by stretch; iii) muscular/urothelial afferents were activated by stretch, urothelial stroking, and von Frey probing; iv) serosal afferents were activated only by von Frey probing and not by either stretch or urothelial stroking. The horizontal lines beneath A and B indicate the onset and termination of stretch (20 s) or von Frey probing (1 g, 3 s) stimuli. Stroking of the urothelium is indicated by dots below the respective records.