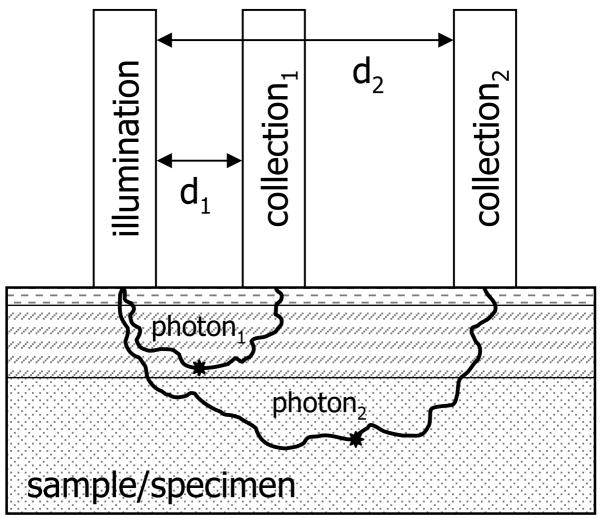
Fig. 1.
Schematic depicting spatially offset Raman spectroscopy. The spatial separation between illumination and collection optics allows depth probing into specimens. Collection optics located at a small distance from the illumination source (d1) will collect Raman scattered light originating in regions near the specimen surface, while collection optics located at a greater distance from the illumination source (d2) will collect scatter originating in deeper layers. The stars represent the points where Raman scattered photons are emitted.