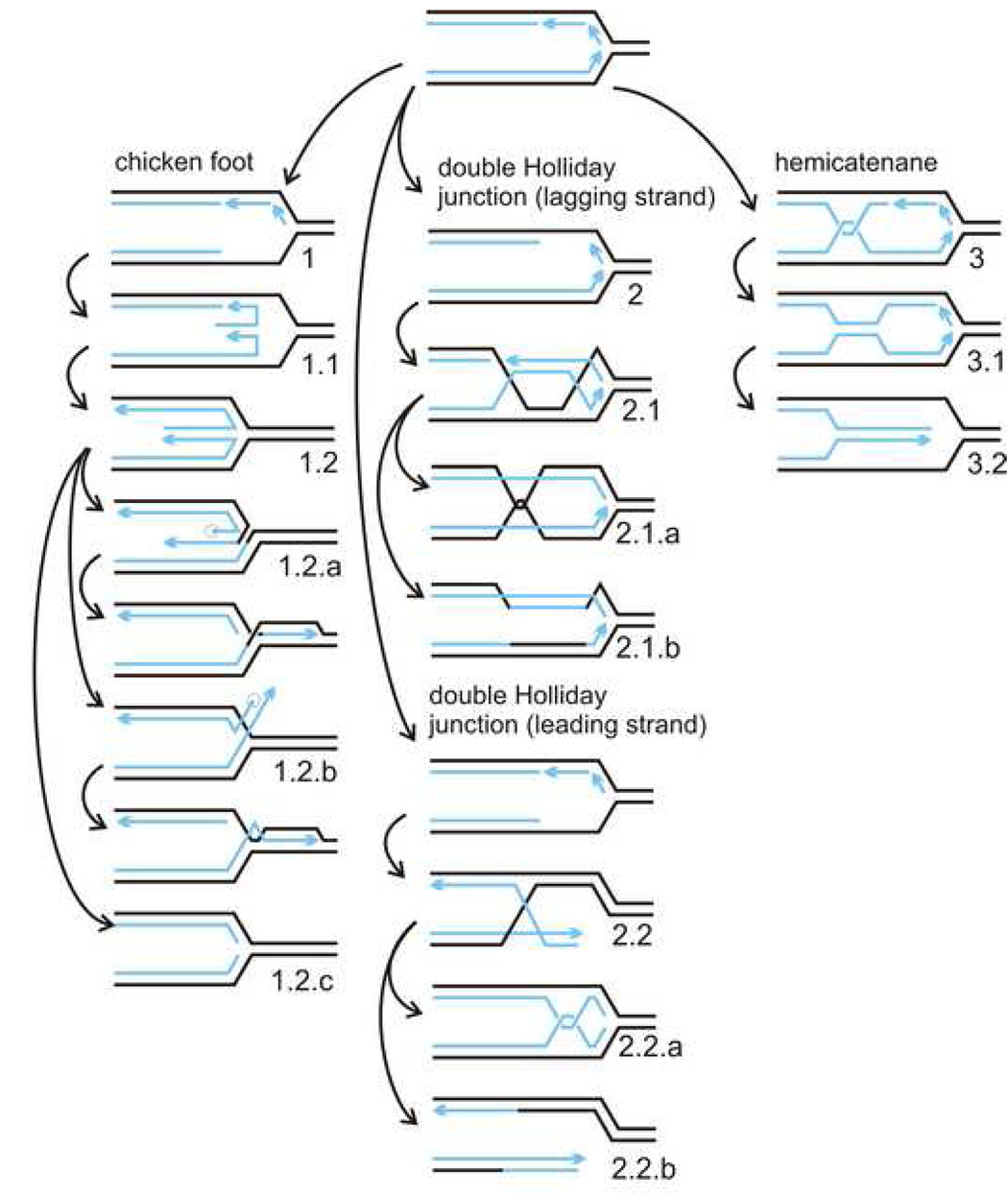
Figure 2. Pathways of replication fork remodeling, via chicken foot (CF), double Holliday junction (double HJ) and hemicatenane (HC) intermediates.
Further processing of these structures can include more than one subpathway (denoted 1.1, 1.2, etc.). Note that the pathway 2.2. can lead to undesirable double strand break intermediates depending on how the double HJ is resolved. Chicken Foot (CF, 1): CF can be simply reversed by unwinding or branch migration, or further processed in one out of three ways: 1.2.a. Resolution with subsequent end processing and strand invasion. 1.2.b. End processing with subsequent strand invasion. 1.2.c. Complete exonucleolytic degradation. Double HJ (2): 2.1. Stand exchange. 2.1.a. Dissolution through branch migration and decatenation. 2.1.b. Resolution. 2.2. Note that resolution applied when leading strand synthesis is blocked can lead to double strand breaks, 2.2.b. Hemicatenane (HC, 3): HC can be reversed by branch migration and decatenation. Alternatively, it can expand into a daughter/daughter duplex (3.1.) and then a chicken foot (3.2.).