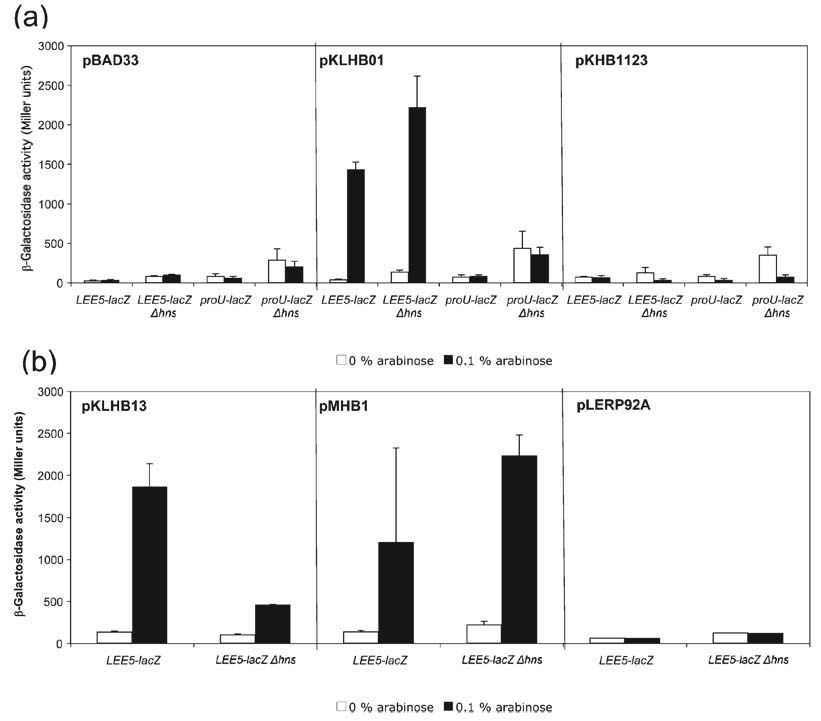
Fig. 2.
Analysis of the Ler N terminus and C terminus. (a) β-Galactosidase activities were derived from K-12 strains containing LEE5–lacZ and proU–lacZ fusions in the presence of the pBAD33 vector, wt Ler or wt H-NS proteins, expressed from plasmids pKLHB01 and pKHB1123, respectively, under the control of the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter. Plasmids were transformed into LEE5–lacZ fusion strains wt for hns (KH4105) or deleted for hns (KH4115); similarly, the above plasmids were transformed into proU–lacZ fusion strains wt for hns (KH4106) and deleted for hns (KH4116). The values are presented in Miller units and represent the mean of at least two independent assays performed in triplicate. Error bars, sd. (b) Plasmid pKLHB13 encodes a recombinant Ler protein containing a C-terminal truncation, missing the last 11 aa compared with H-NS. Plasmid pMHB1 encodes a protein containing the first 21 aa of H-NS, containing α-helices 1 and 2, fused to the N terminus of Ler (see Fig. 1). Plasmid pLERP92A contains a mutated Ler protein with the point mutation P92A within the core DNA binding motif.