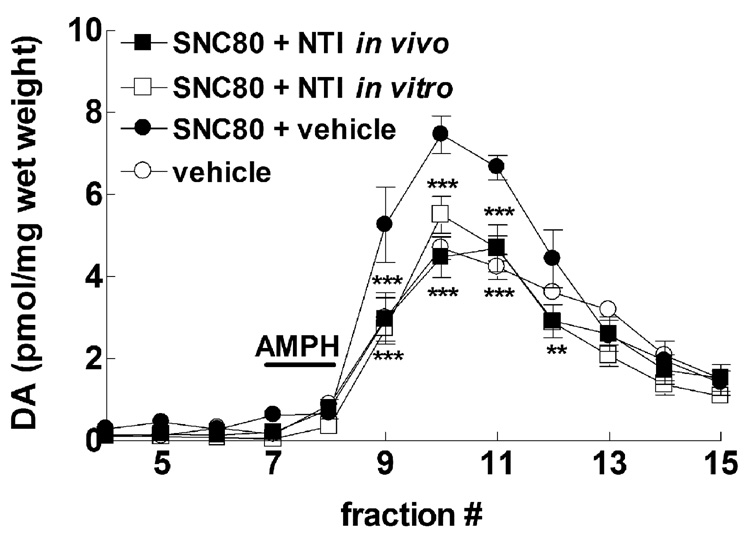
Fig. 3.
In vivo and in vitro administration of the delta selective antagonist NTI diminishes the ability of in vivo SNC80 to enhance amphetamine-mediated dopamine efflux. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected (s.c.) with vehicle alone, 10 mg/kg SNC80 alone, or 1.0 mg/kg NTI 30 min after SNC80 administration (in vivo NTI). Striatal preparations were made from all groups 3h after the vehicle or SNC80 injections, and perfused with buffer for 30 min before challenge with 100 µM amphetamine sulfate for 5 min. Some preparations from SNC80 treated rats were perfused with 10 nM NTI for 30 min prior to amphetamine challenge (in vitro NTI). The dopamine content of the fractions from all groups were assessed by HPLC-electrochemical detection, as described in the Methods, and reported as pmol of dopamine per mg wet weight ± S.E.M (n = 4 in duplicate). Statistical significance for values was determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison analysis. **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to SNC80 + vehicle.