Figure 2. Lack of functional stem cells in K5Cre;itgb1F/F epithelium.
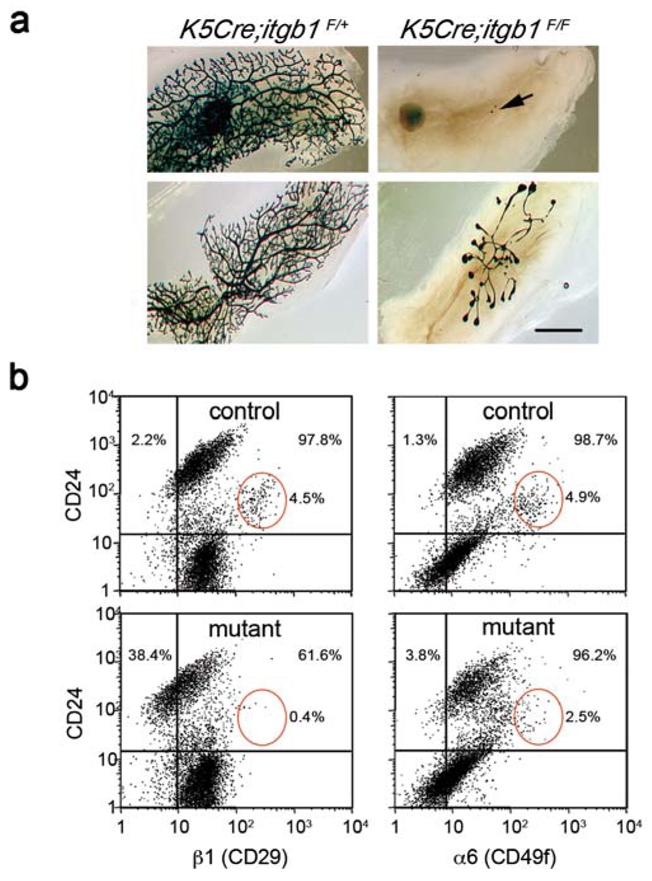
(a) Whole-mount X-gal staining of the secondary outgrowths produced by control K5Cre;itgb1F/+ and mutant K5Cre;itgb1F/F epithelium in the cleared fat pads of virgin recipient mice.
The outgrowths were analysed 10 weeks after transplantation. Arrow (upper panel) indicates small pieces of transplanted mutant epithelium that did not develop any secondary outgrowth. Lower panel shows the most developed mutant outgrowth and corresponding control. Scale bar, 3 mm.
(b) Flow cytometry analysis of mammary epithelial cells isolated from outgrowths developed by control (upper panels) and mutant (lower panels) epithelium in 12-week-old virgin recipient mice. Cells were stained for CD24 and β1 integrin (left) or CD24 and α6 integrin expression (right). Only CD45−CD31− cells were included in the analysis. Red ellipses show CD24-positive/β1-high and CD24-positive/α6-high cell populations. The percentages of β1- and α6-negative (left to vertical reference line) and positive (right to vertical reference line) cells were calculated for the CD24- positive population (above horizontal reference line) comprising mammary epithelial cells13.
