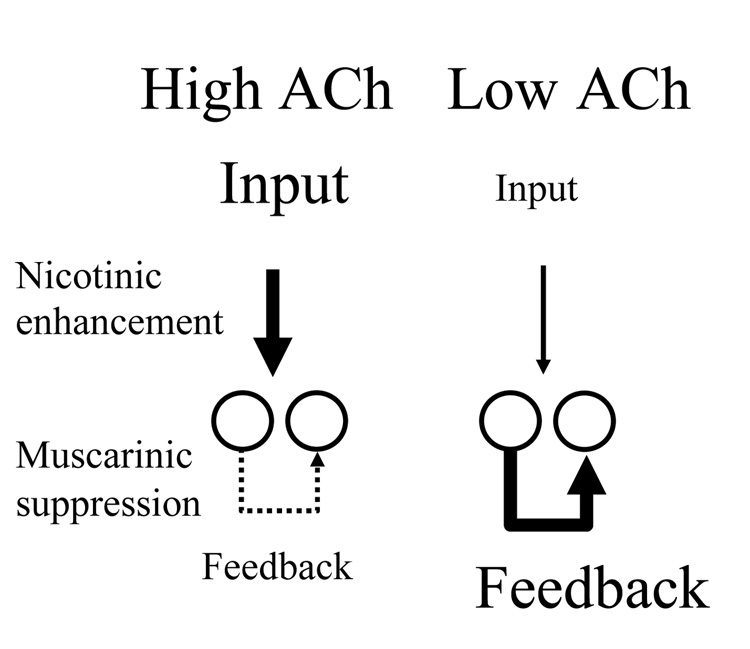
Figure 1.
Effect of acetylcholine on cortical dynamics. Left: High acetylcholine (ACh) levels enhance the magnitude of afferent input to cortex through action at nicotinic receptors. High ACh also suppresses the magnitude of feedback excitation in cortex via presynaptic inhibition of glutamate release. Right: Low acetylcholine levels result in a weaker influence of afferent input relative to the strength of excitatory feedback.