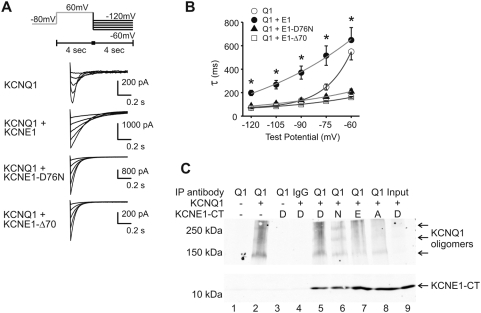
Figure 4. Deactivation rates are accelerated by both KCNE1-D76N and KCNE1-Δ70.
A) Current traces, with deactivation protocol in inset, and B) rates of deactivation plotted against voltage from CHO cells transiently expressing KCNQ1 (Q1) either without KCNE1 (E1), or with wild-type E1, E1-D76N, or E1-Δ70. Asterisks (*) indicate significant change between wild-type E1 and both E1 mutations. n = 6. C) Co-immunoprecitation experiment of C-termini KCNE1 with full length KCNQ1. Full length KCNQ1 was expressed with KCNE1 C-terminus (KCNE1-CT), either wild-type or with D76E, D76N, or D76A point mutations. Immunoprecipitation was performed with goat anti-KCNQ1 antibody, and immunoblot with rabbit anti-FLAG antibody (Santa Cruz). For controls, lane 1 shows results from untransfected cells, lane 2 from KCNQ1 alone, lane 3 from KCNE1 wild type (D76) alone, and lane 4 from KCNQ1 and KCNE1 with control antibody. The different KCNE1 forms are designated by the single amino acid letter at the 76th position.