FIG. 2.
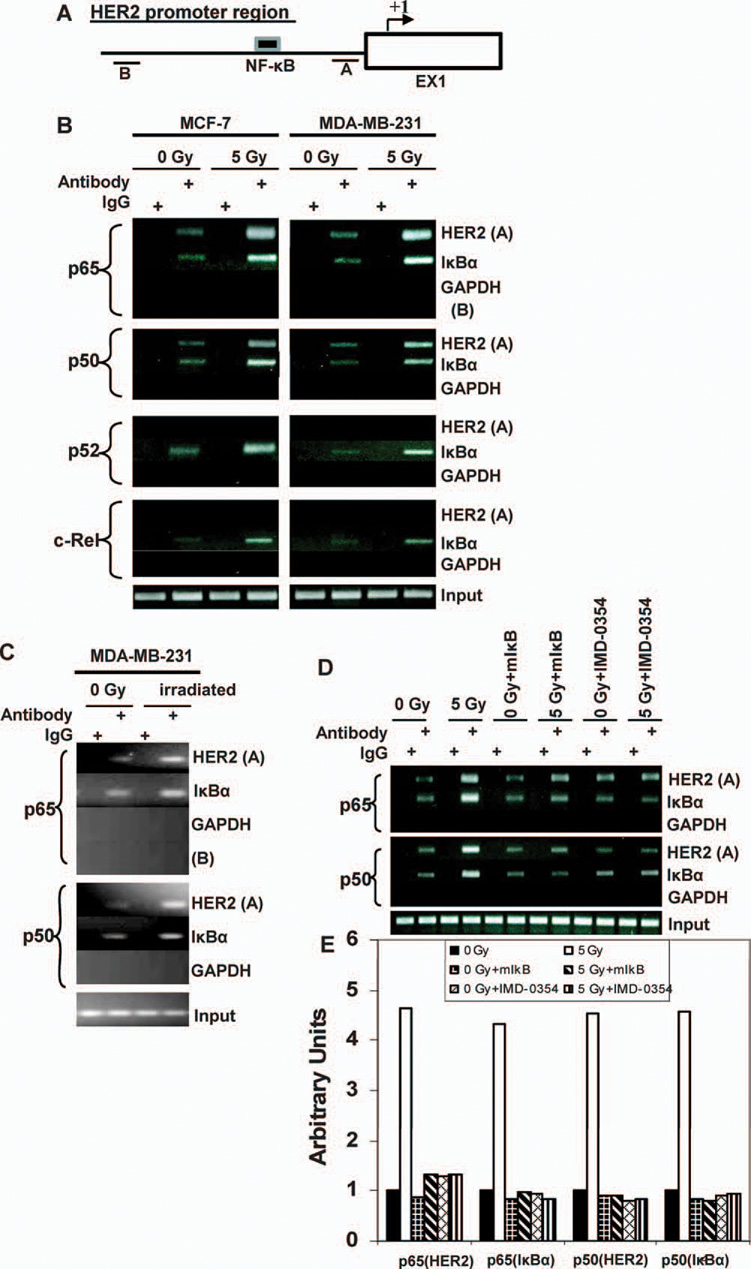
Gamma-radiation exposure enhanced the recruitment of NF-κB to HER2 promoter. Panel A: Schematic of the HER2 promoter locus of two fragments (A and B) studied by ChIP assays. Panel B: Chromatin of control and irradiated MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells was immunoprecipitated with antibodies to p65, p50, p52 and c-Rel or mouse IgG. Both fragments A and B were amplified by PCR, and total chromatin (total input) was positive control for PCR. The PCR fragment of the IκBα promoter region (−1134/−902) and GAPDH were also included as positive and negative controls, respectively. Panel C: Sham-irradiated and γ-irradiated MDA-MB-231 xenografts were examined for recruitment of p65 and p50 to the HER2 promoter (fragment A) and IκBα promoter (NF-κB positive control) by ChIP assays. Fragment B l was included as the negative control. Panel D: MCF-7 cells were preincubated with 2 µM NF-κB inhibitor, IMD-0354 or DMSO (as solvent control) for 5 h or were transiently transfected with mutant IκBα before exposure to 5 Gy or sham irradiation. Recruitment of p65 and p50 to the HER2 promoter (fragment A) and IκBα promoter (NF-κB positive control) were examined by ChIP assays. Panel E: The reduction of binding of NF-κB to the HER2 and IκBα promoters by different inhibitors was estimated by densitometry normalized to the input band.
