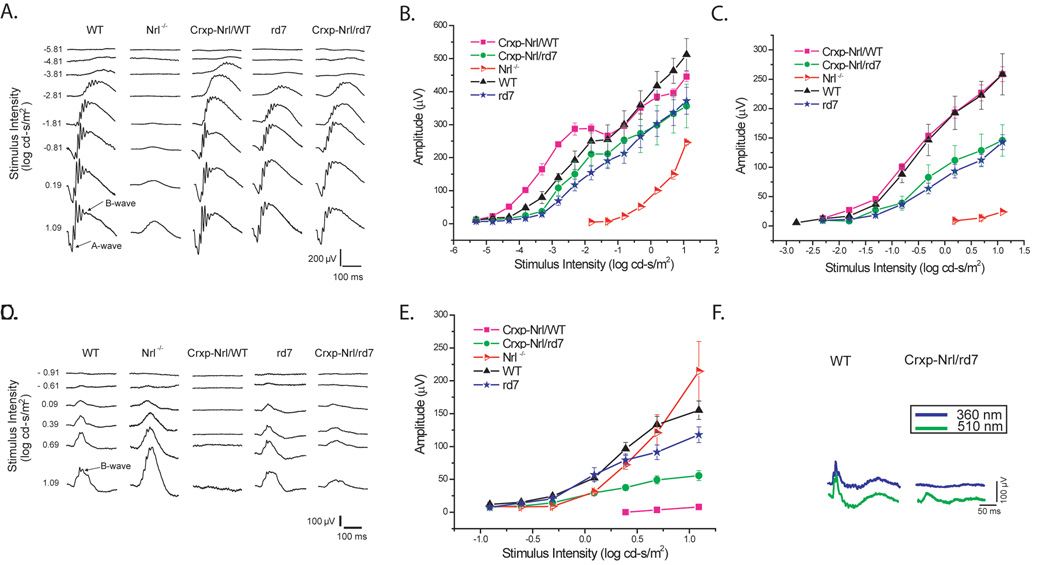
Figure 4. Absence of normal cone function in cone photoreceptors expressing NRL but not NR2E3.
(A) Representative dark-adapted ERGs for increasing stimulus intensities are shown for WT, Nrl−/−, Crxp-Nrl/WT, rd7 and Crxp-Nrl/rd7 mice at two months age. Intensity-response functions for the (B) a-wave and (C) b-wave amplitude were plotted on log-linear coordinates. (D) Representative light-adapted ERGs waveforms with increasing stimulus intensity for WT, Nrl−/−, Crxp-Nrl/WT, rd7 and Crxp-Nrl/rd7 mice, as indicated. (E) Plots of the b-wave amplitude as a function of stimulus intensity for light-adapted conditions. At 2 months of age, there was no significant difference in the photopic response between WT and rd7 mice. (D–E) B-wave amplitude at the maximum intensity for the Crxp-Nrl/rd7 mice. A reduction of about 40% is observed from the WT and rd7 mice. (F) Representative light-adapted S- (360 nm) and M- (510 nm) cone ERGs showing a smaller M-cone response and undetectable S-cone response in Crxp-Nrl/rd7 mice compared to WT mice. Bars indicate ± standard error.