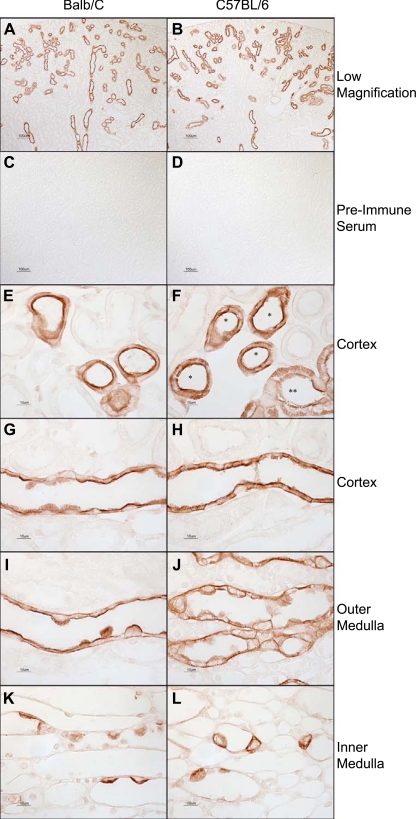
Fig. 2.
Distribution of Rhcg in mouse kidney using Rhcg antibody B. A and B: low-magnification micrographs of Rhcg immunolabel in Balb/c (A) and C57BL/6 (B) kidney using antibody B. Rhcg immunolabel is present in a subpopulation of renal epithelial cells, consistent with previous demonstration in DCT, connecting tubule (CNT), initial collecting tubule (ICT), and CCD. Antibody B was used at a dilution of 1:10,000 in these studies. C and D: substitution of preimmune sera for antibody B. No detectable immunolabel is present in either Balb/c (C) or C57BL/6 (D) kidneys. E: connecting segments in Balb/c mouse kidney. Strong apical and faint basolateral immunolabel are present. F: connecting segment (*) and DCT (**) in a C57BL/6 mouse kidney. Both apical and basolateral Rhcg immunolabel are easily evident. G: CCD in a Balb/c mouse kidney. Strong apical and weak basolateral immunolabel are present. H: CCD from a C57BL/6 mouse kidney. Both strong apical and strong basolateral immunolabel are present. I: OMCD from a Balb/c kidney. Apical immunolabel is easily evident; basolateral immunolabel is of lesser intensity. J: OMCD in a C57BL/6 mouse kidney. Both apical and basolateral Rhcg immunolabel are relatively strong. K: IMCD in the Balb/c kidney. Strong apical and weak basolateral immunolabel are evident. L: IMCD from a C57BL/6 kidney, where both strong apical and basolateral Rhcg immunolabel are present. The same dilution of antisera or preimmune sera, 1:10,000, was used in all experiments. Results are representative of findings in at least 6 mice.