Fig. 1.
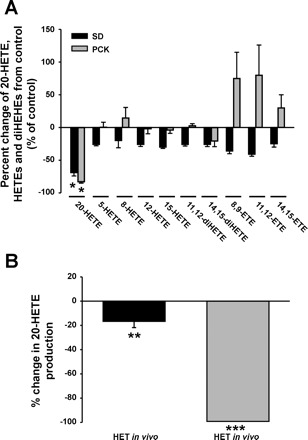
Inhibition of 20-HETE production in cystic PCK vs. noncystic Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat kidneys. A: HET-0016 (10 mg/kg) was administered acutely into the intraperitoneal space 90–120 min before death. Renal microsomes were isolated as described in materials and methods, and a cytochrome P-450 assay was performed and analyzed by liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). The data was graphed as a ratio of HET-treated vs. vehicle-treated rats (i.e., percent change from vehicle-treated control). *P < 0.001 significance between the PCK and SD rats treated with vehicle vs. HET-0016; n = 3–4 rats/eicosanoid group. B: LC/MS was performed on rat renal microsomes harvested from chronically treated PCK rats with vehicle or HET-0016 (HET) and graphed as percent change from the vehicle group (black bar). Renal microsomes were incubated with HET-0016 (1 μM) during the incubation phase and analyzed for 20-HETE synthesis inhibition in vitro (grey bar); n = 3–4 samples/group. **P < 0.05 significance between chronic vehicle- vs. HET-0016-treated kidneys. ***P < 0.001 significance between kidney samples treated with vehicle or HET-0016 during in vitro P450 assay.
