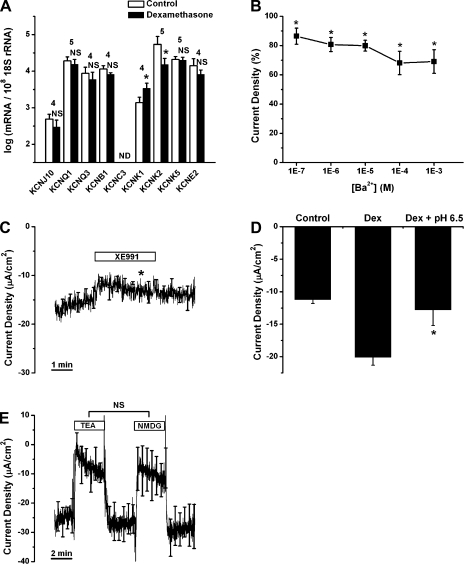
Fig. 6.
Regulation of K+ channel transcript expression by dexamethasone and effects of K+ channel blockers on current density. A: qRT-PCR evaluation of transcript expression of KCNJ10, KCNQ1, KCNQ3, KCNB1, KCNC3, KCNK1, KCNK2, KCNK5, and KCNE2 in Reissner's membrane in the absence and presence of dexamethasone (100 nM for 24 h). Transcripts were quantified relative to 18S rRNA in Reissner's membrane. Values are means ± SE (n = 4–5); numbers above bars represent number of qRT-PCRs. ND, no detectable transcript expression. NS, not significant (i.e., <1.5-fold change). *P < 0.05 (>1.5-fold difference between absence and presence of dexamethasone). B: concentration-response curve for decrease of current density by Ba2+. Values are means ± SE (n = 5). *P < 0.05, before vs. during Ba2+ application. C: effect of XE-991 (100 μM, n = 4) on current density. Averages of all experiments are shown; SE is drawn only at intervals for clarity. *P < 0.05, 1 min before vs. 2.5 min after XE-991 application. D: decrease in dexamethasone-stimulated current density caused by exposure to pH 6.5. Values are means ± SE (n = 4). *P < 0.05, 1 min before vs. 2.5 min after application of pH 6.5 solution. E: effect of tetraethylammonium Cl (TEA, 30 mM, n = 5) on current density compared with that of equimolar N-methyl-d-glucamine-Cl (NMDG). Averages of all experiments are shown; SE is drawn only at intervals for clarity.