Figure 1.
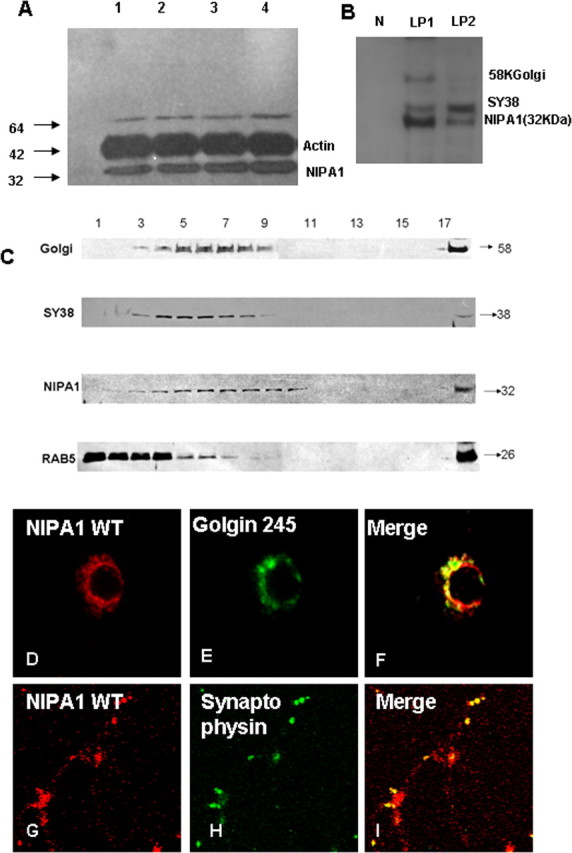
Distribution of endogenous NIPA1 protein in the mammalian CNS. Western blot analysis of NIPA1 distribution in adult mouse brain demonstrating the presence of endogenous NIPA1 protein in cortical regions (A, lane 1), cerebellum (lane 2), striatum (lane 3), and cervical spinal cord (lane 4); there was no significant differences between these regions when compared with actin load (plotting not shown). Fractionation with synaptosome isolation (B) showed, as suggested by the results shown in C, the presence of NIPA1 in the LP1 fraction, containing large membranes, such as Golgi complex (58KGolgin); additionally, we observed NIPA1 presence in the LP2 fraction, which is enriched for synaptic vesicles (SY38 synaptophysin) and small transport vesicles; the nuclear fraction (N lane) did not show any NIPA1 reactivity. Results obtained from mouse and rat adult brains did not differ in regional or subcellular distribution (data not shown). C, Western blot analysis of subcellular fractions of adult mouse brain. Antibodies against NIPA1 revealed the overlap of peak fractions with the Golgi complex markers and synaptophysin (SY38), while there was no peak fracture overlap with early endosomal markers (Rab5). Immunocytochemistry using E18 rat cultured cortical neurons confirmed colocalization of endogenous NIPA1 (red) with Golgi complex (green) (D–F) marker Golgin 245 and synaptic vesicle marker synaptophysin (G–I).
