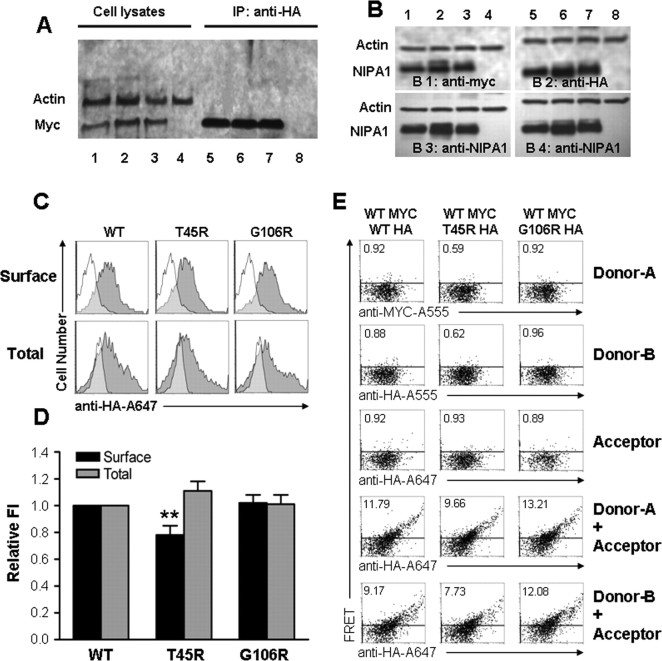
Figure 5.
Expression and trafficking of NIPA1. Coimmunoprecipitation of NIPA1::HA and NIPA1::myc using anti-HA antibodies showed similar amount of precipitated protein between the expressed mixture of NIPAWT::HA and NIPAWT::myc (A, lanes 1 and 5), NIPA1WT::myc and NIPA1T45R::HA (A, lanes 2 and 6), or NIPA1WT::myc and NIPA1G106R::HA (A, lanes 3 and 7; lanes 4 and 8 are negative control with empty vector transfection). The ratio of myc and HA signal did not significantly differ (plotting not shown). The amount of expressed in HEK293 cells did not differ between various tagging of WT NIPA1 (B, lanes 1 and 5 contain equimolar amounts of NIPA1WT::HA and NIPA1WT::myc), or between WT and mutant forms (lanes 2 and 6 contain NIPA1WT NIPA1WT::myc and NIPA1T45R::HA, lanes 3 and 7 NIPA1WT::myc and NIPA1G106R::HA, lanes 4 and 8 empty vector; B1 is stained with anti-myc antibodies, B2 with anti-HA antibodies, and B3 and B4 with anti-NIPA1 antibodies). The ratio of anti-HA, anti-myc, and anti-NIPA1 antibodies signal did not differ when corrected for actin load (plotting not shown). Representative flow cytometry frequency histograms of Alexa-647 (A647) fluorescence intensity for cells expressing NIPA1WT::HA (left), NIPA1T45R::HA (middle), or NIPA1G106R::HA (right) constructs and stained with the HA-A647 antibody (C). A representative histogram from mock transfected cells (white) was overlaid on each of the histograms from positively transfected cells (gray). Surface staining (i.e., without membrane permeabilization) is shown in the top row, and total cellular staining (i.e., after membrane permeabilization) is shown in the bottom row. The x-axis indicates arbitrary fluorescence units (log scale), and the y-axis indicates the number of cells. D, Plotting of cell surface localization using HA tagging and detected by flow cytometry. Data is normalized to the signal from WT NIPA1 protein. Surface signal was compared with a total signal, which paralleled the pattern of activity on the cell surface. Only the T45R mutation had a mild reduction of surface activity with normal total amount of protein (**p < 0.01 compared with the wild-type condition). E, Representative flow cytometry dot plots of cells expressing an equal mixture of NIPA1WT::myc and NIPA1WT::HA (left), NIPA1T45R::HA (middle), or NIPA1G106R::HA (right) constructs and stained with various combinations of A555- or A647-conjugated antibodies. In the first three rows, cells were stained with the MYC-A555 (Donor-A), HA-A555 (Donor-B), or HA-A647 (Acceptor) antibodies, illustrating that spectral compensation with respect to the FRET channel was performed appropriately. In the last two rows, cells were costained with the HA-A647 antibody and either the MYC-A555 (fourth row) or the HA-A555 (fifth row), allowing for FRET to be evaluated between MYC- and HA-tagged proteins or between HA-tagged proteins, respectively. The horizontal line in each panel indicates the FRET gate, such that <1% of cells were deemed FRET positive when stained with A555- or A647-conjugated antibodies individually (the percentage positive is shown in the top right of each panel).